Martin, Marginal contrast in loanword phonology: Production and perception
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 10 abril 2025
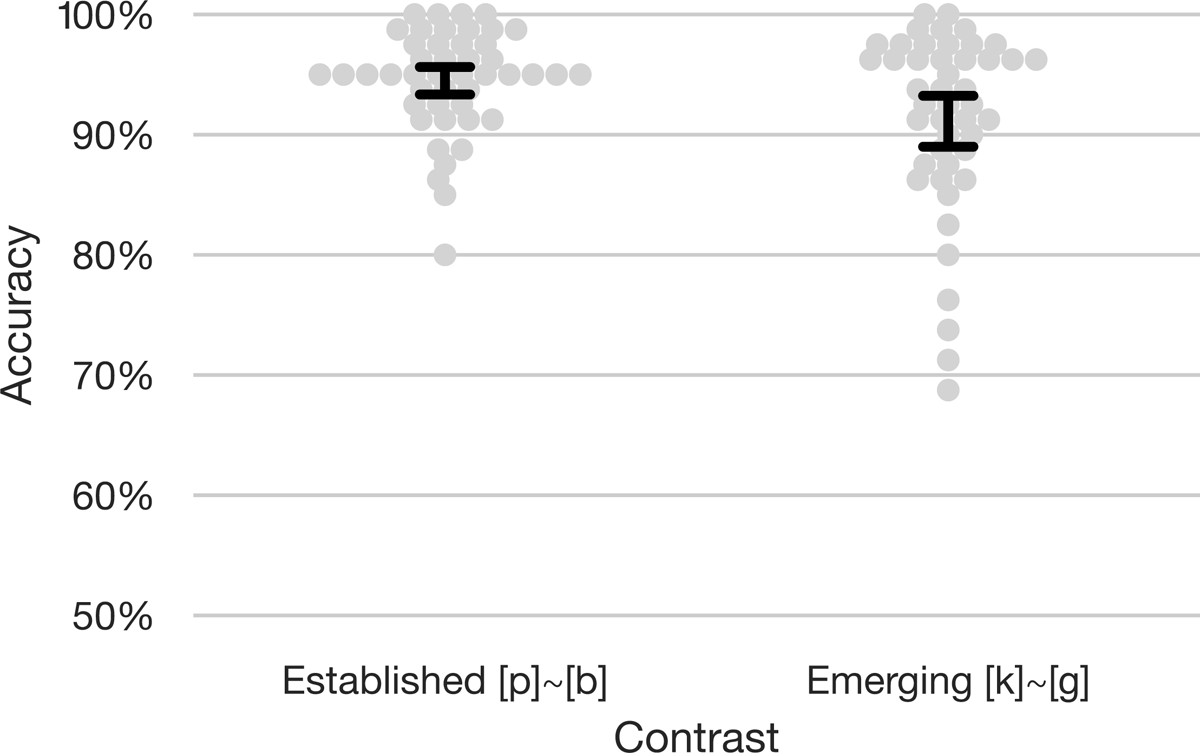
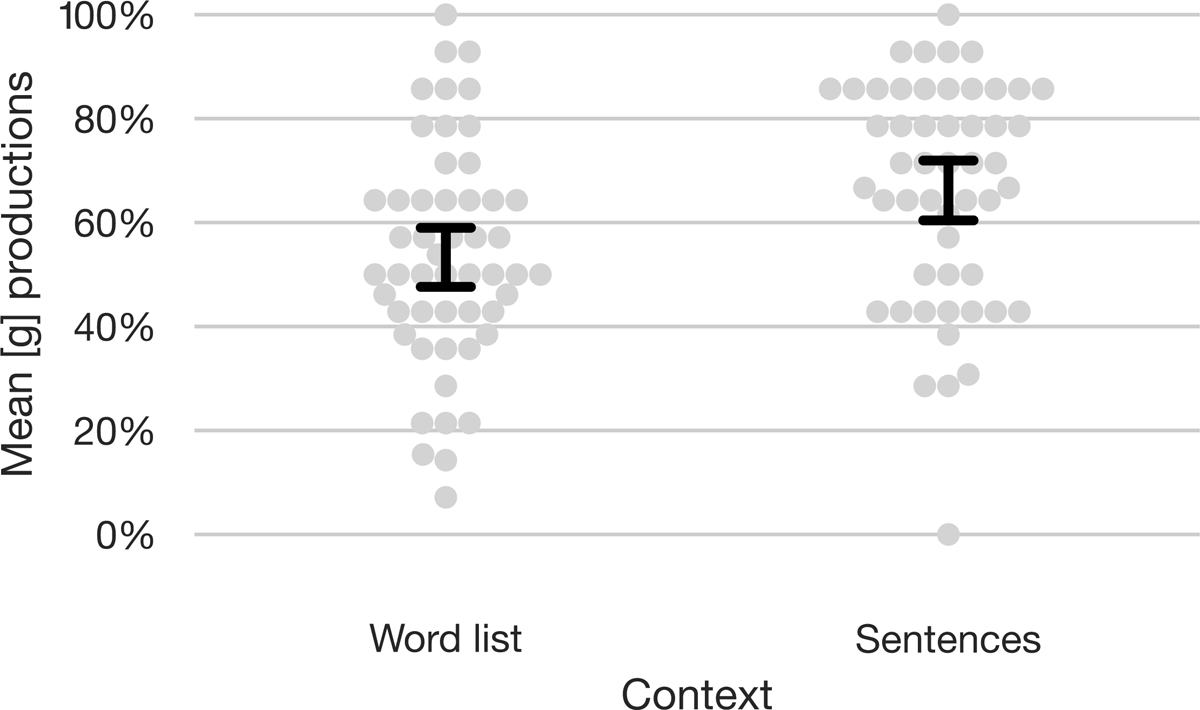
Though Dutch is usually described as lacking a voicing contrast at the velar place of articulation, due to intense language contact and heavy lexical borrowing, a contrast between /k/ and /g/ has recently been emerging. We explored the status of this contrast in Dutch speakers in both production and perception. We asked participants to produce loanwords containing a /g/ in the source language (e.g., goal) and found a range of productions, including a great many unadapted [g] tokens. We also tested the same speakers on their perception of the emerging [k] ~ [g] contrast and found that our participants were able to discriminate the emerging contrast well. We additionally explored the possibility that those speakers who use the new contrast more in production are also better at perceiving it, but we did not observe strong evidence of such a link. Overall, our results indicate that the adoption of the new sound is well advanced in the population we tested, but is still modulated by individual-level factors. We hold that contrasts emerging through borrowing, like other phonological contrasts, are subject to perceptual and functional constraints, and that these and other ‘marginal contrasts’ must be considered as full-fledged parts of phonology.

Most borrowable segments in SEGBO

The phonetics and phonology of Uspanteko (Mayan) - Bennett - 2022
Martin Marginal contrast in loanword phonology: Production and

Highest frequency and lowest frequency loanwords Most frequently
Martin Marginal contrast in loanword phonology: Production and
PDF) Marginal contrast in loanword phonology: Production and
Martin Marginal contrast in loanword phonology: Production and
Laboratory Phonology Issue: Issue: 1(13) Volume 13 (2022)

Perception of illusory clusters: the role of native timing
Laboratory Phonology Issue: Issue: 1(13) Volume 13 (2022)

PDF] Phonetic Distinctiveness vs. Lexical Contrastiveness in Non

The dynamical landscape: phonological acquisition and the

Vowel spaces for speakers ItF15, ItF13, and ItF11; stressed mid

Percent Prevoiced /ɡ/ by Language and Group Aggregated by Child
Languages, Free Full-Text
Recomendado para você
-
 Mexico - Wikipedia10 abril 2025
Mexico - Wikipedia10 abril 2025 -
 Rule 63, Teh Meme Wiki10 abril 2025
Rule 63, Teh Meme Wiki10 abril 2025 -
 Tig Bitties on Tumblr10 abril 2025
Tig Bitties on Tumblr10 abril 2025 -
 Somebody sent me this, what does it even mean? I looked up on google and urban dictionary said ''my little vampire''? The whole sentence makes no sense, am I missing something?10 abril 2025
Somebody sent me this, what does it even mean? I looked up on google and urban dictionary said ''my little vampire''? The whole sentence makes no sense, am I missing something?10 abril 2025 -
urban-dictionary-word-list/data/U.data at master · mattbierner/urban- dictionary-word-list · GitHub10 abril 2025
-
 The Kpop Dictionary: 500 Essential Korean Slang Words and Phrases Every Kpop Fan Must Know10 abril 2025
The Kpop Dictionary: 500 Essential Korean Slang Words and Phrases Every Kpop Fan Must Know10 abril 2025 -
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/independent-contractor.asp-FINAL-6904c017dfbf4da18e90cf4db4af91e7.png) Independent Contractor: Definition, How Taxes Work, and Example10 abril 2025
Independent Contractor: Definition, How Taxes Work, and Example10 abril 2025 -
 Heritage, Free Full-Text10 abril 2025
Heritage, Free Full-Text10 abril 2025 -
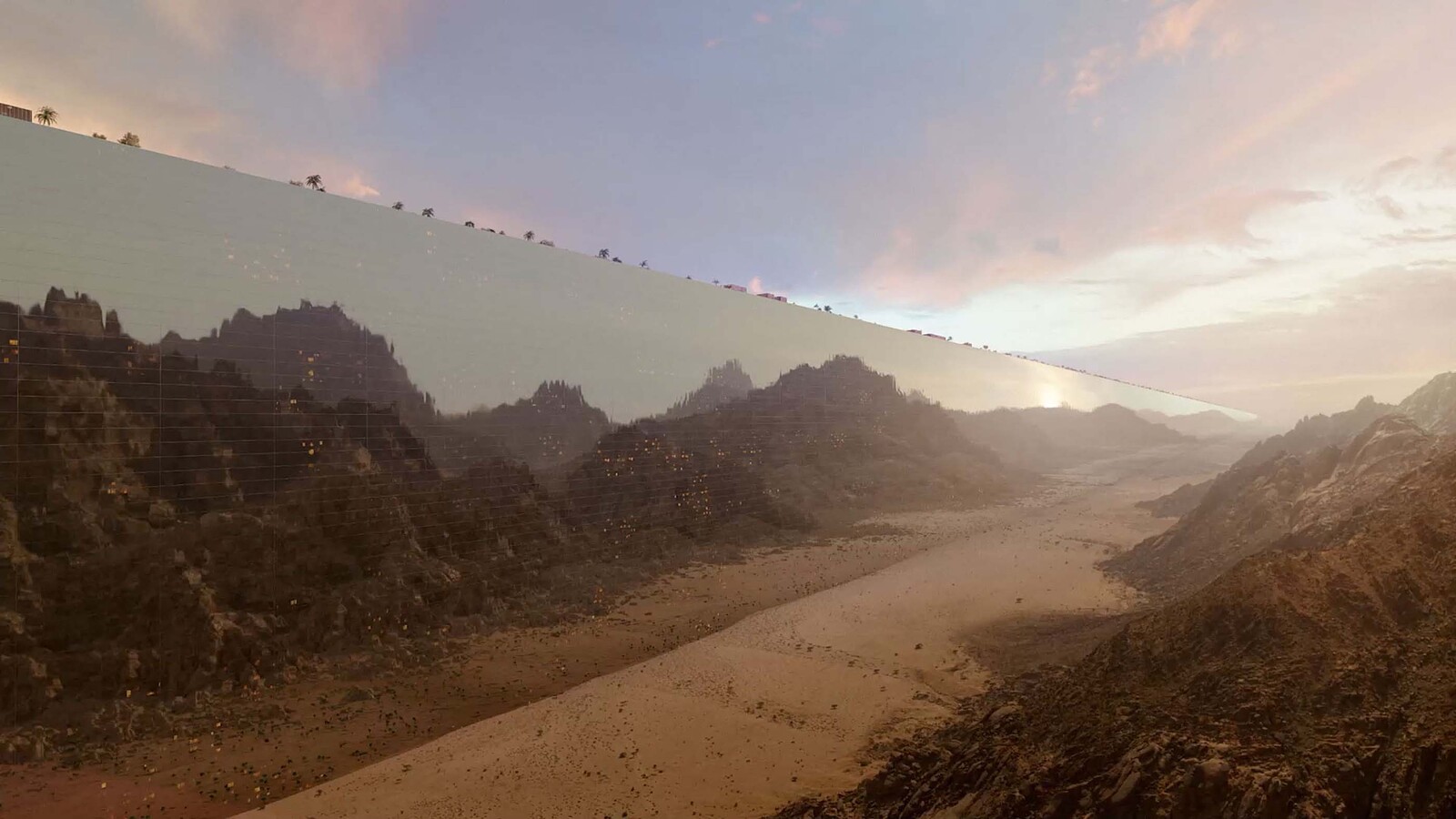 Horizons - Gökçe Günel - New Wonders for the World10 abril 2025
Horizons - Gökçe Günel - New Wonders for the World10 abril 2025 -
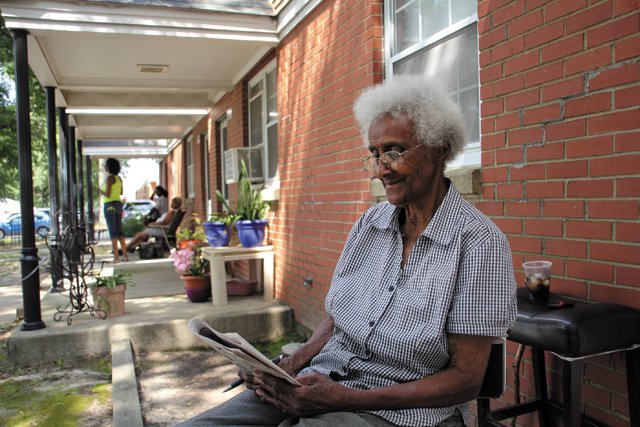 To Live and Die in Creighton Court10 abril 2025
To Live and Die in Creighton Court10 abril 2025
você pode gostar
-
/cloudfront-us-east-1.images.arcpublishing.com/eluniverso/V3IQ3R3CKLZNVRREEE4BRWNRWQ.jpg) Nacional, de Luis Suárez y el técnico Pablo Repetto, campeón del Clausura uruguayo, Fútbol, Deportes10 abril 2025
Nacional, de Luis Suárez y el técnico Pablo Repetto, campeón del Clausura uruguayo, Fútbol, Deportes10 abril 2025 -
 Pet Shop Boys Dreamworld The Greatest Hits Live Unisex T-Shirt10 abril 2025
Pet Shop Boys Dreamworld The Greatest Hits Live Unisex T-Shirt10 abril 2025 -
 KREA - a realistic vampire bat steel mask, epic scale, character concept art, face symmetry, intricate accurate details, artstation trending, octane render, cinematic color grading, soft light, rule of thirds, golden ratio10 abril 2025
KREA - a realistic vampire bat steel mask, epic scale, character concept art, face symmetry, intricate accurate details, artstation trending, octane render, cinematic color grading, soft light, rule of thirds, golden ratio10 abril 2025 -
 Jogo baseado em 'O Massacre da Serra Elétrica' será lançado nesta10 abril 2025
Jogo baseado em 'O Massacre da Serra Elétrica' será lançado nesta10 abril 2025 -
 I love Sonic's design in Sonic Mania. Definitely one of my faves.10 abril 2025
I love Sonic's design in Sonic Mania. Definitely one of my faves.10 abril 2025 -
 Majutsushi Orphen Hagure Tabi Urbanrama-hen Episode 01 Subtitle Indonesia - BiliBili10 abril 2025
Majutsushi Orphen Hagure Tabi Urbanrama-hen Episode 01 Subtitle Indonesia - BiliBili10 abril 2025 -
I got you, baby girl. Joel, Ellie and one of the best scenes from10 abril 2025
-
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/catskills-drive-59bf0d4968e1a2001444db0a.jpg) Catskills Scenic Drive A Backroads Driving Tour10 abril 2025
Catskills Scenic Drive A Backroads Driving Tour10 abril 2025 -
 Heroes of Destiny: Fantasy RPG by MY COM10 abril 2025
Heroes of Destiny: Fantasy RPG by MY COM10 abril 2025 -
 Gismart and Snapchat have made a multi-game partnership to10 abril 2025
Gismart and Snapchat have made a multi-game partnership to10 abril 2025
