Differential cellular stiffness contributes to tissue elongation on an expanding surface
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 14 abril 2025

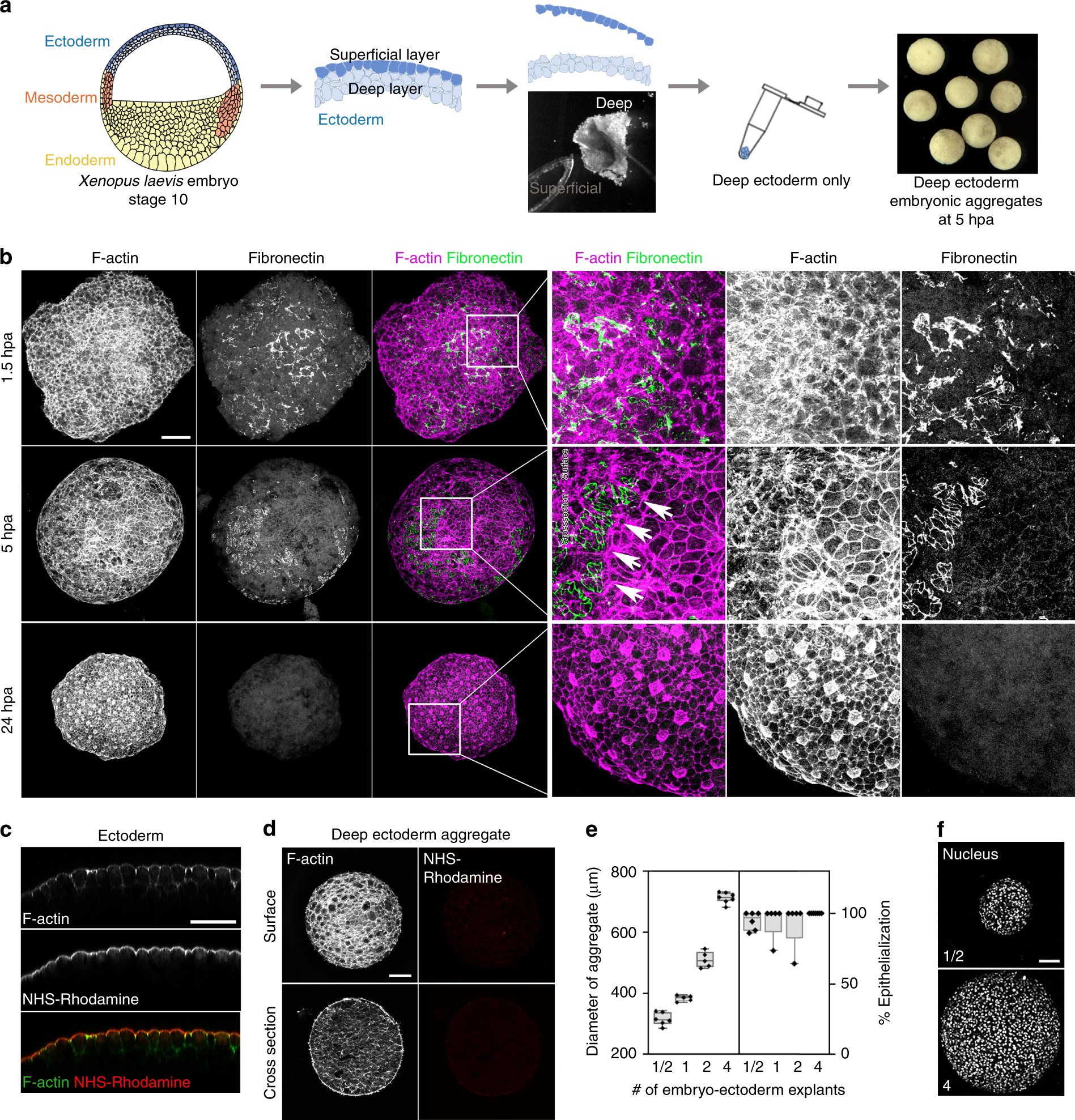
Tissue mechanics drives regeneration of a mucociliated epidermis on the surface of Xenopus embryonic aggregates
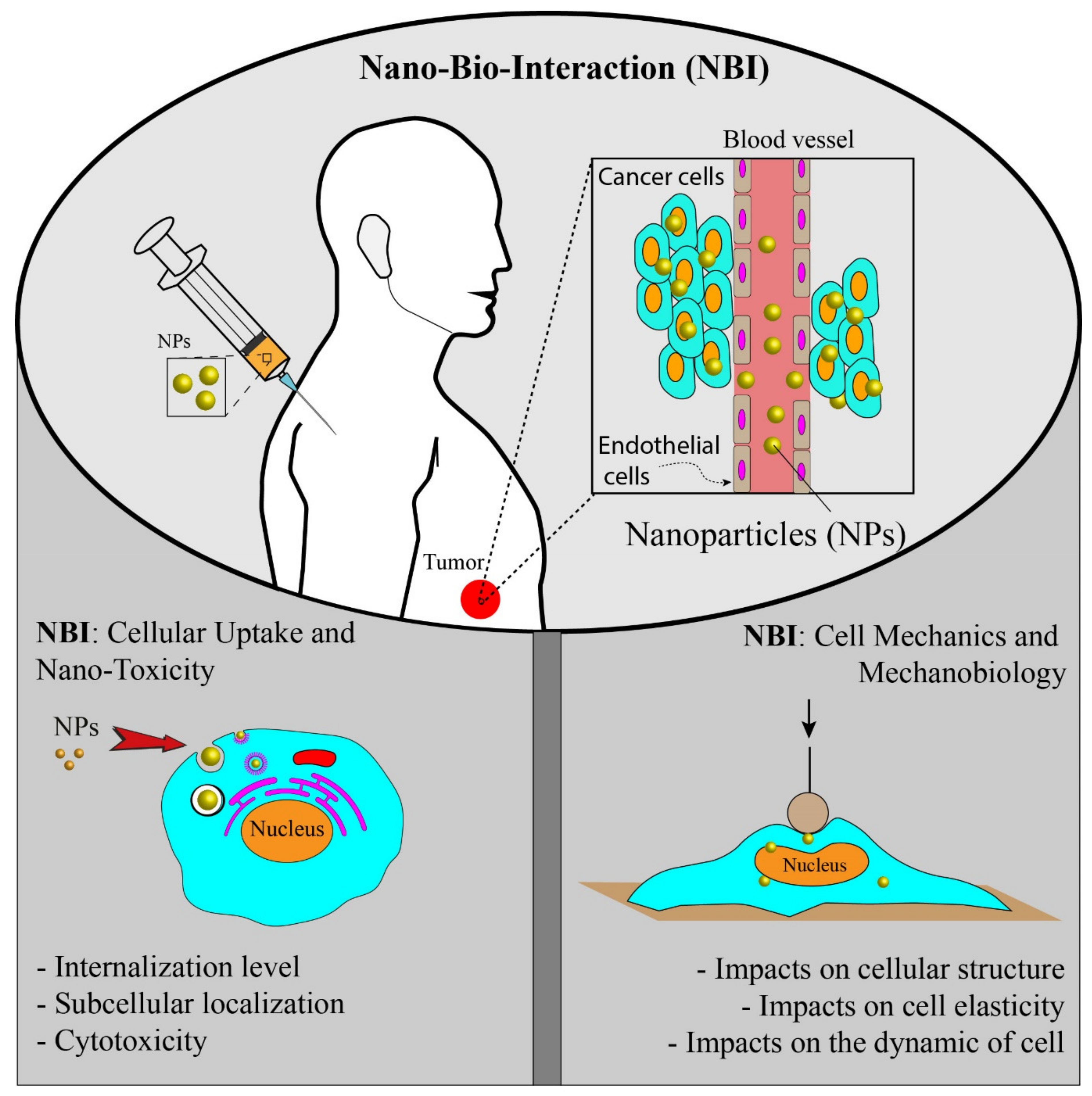
IJMS, Free Full-Text
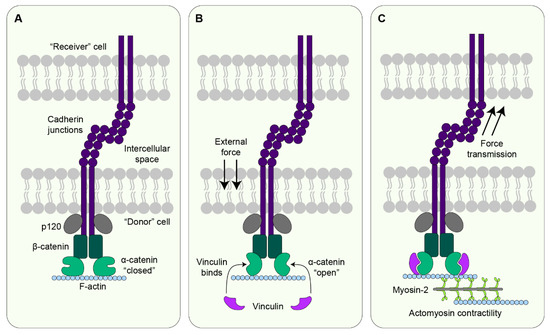
JDB, Free Full-Text

Role of mechanical input from the extra-embryonic EVL in directing
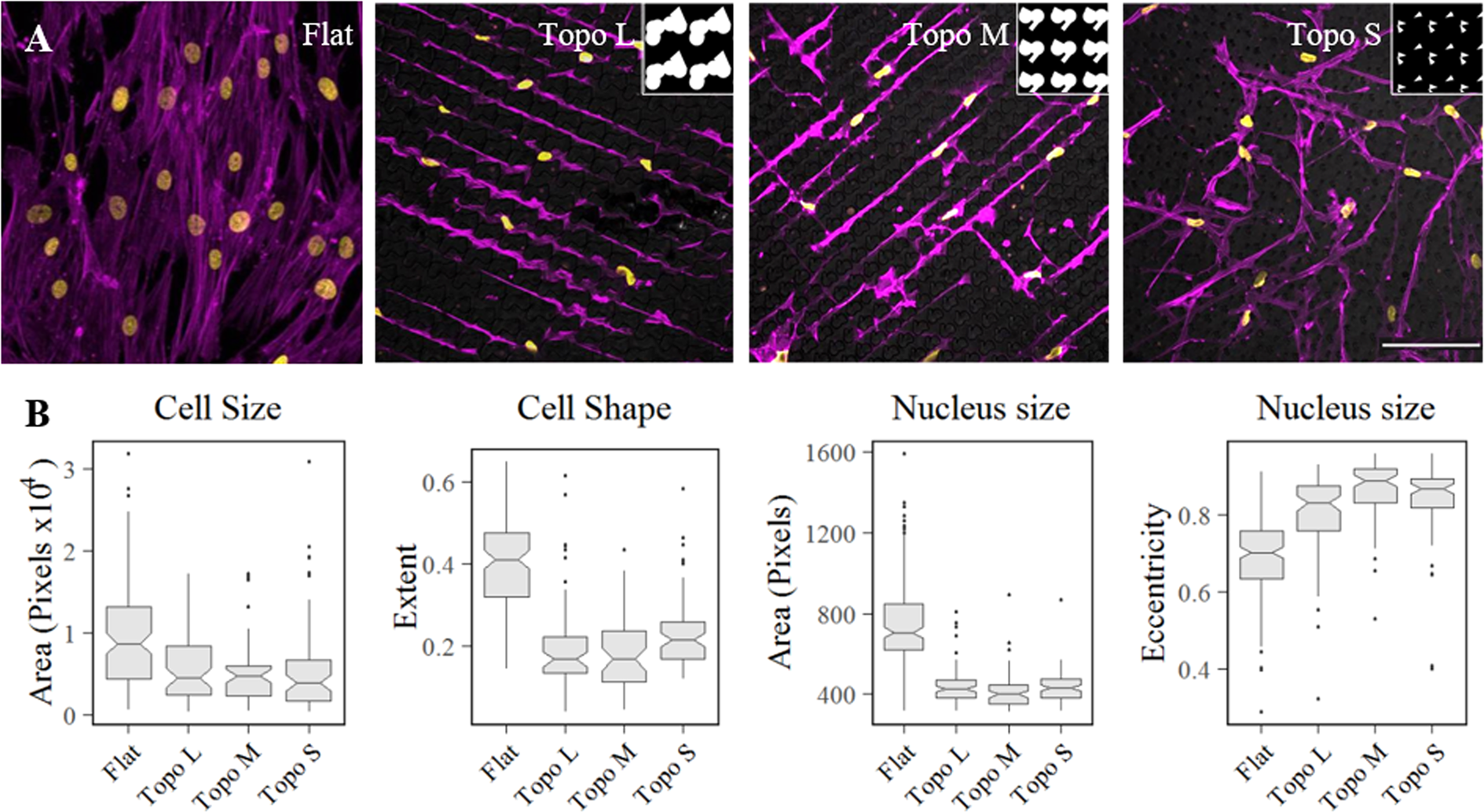
Dynamic adaptation of mesenchymal stem cell physiology upon exposure to surface micropatterns

Increase of Cortical Tension and Stiffness during Normal Gastrulation

Strategic outline of interventions targeting extracellular matrix for promoting healthy longevity

Topography-Mediated Fibroblast Cell Migration Is Influenced by Direction, Wavelength, and Amplitude
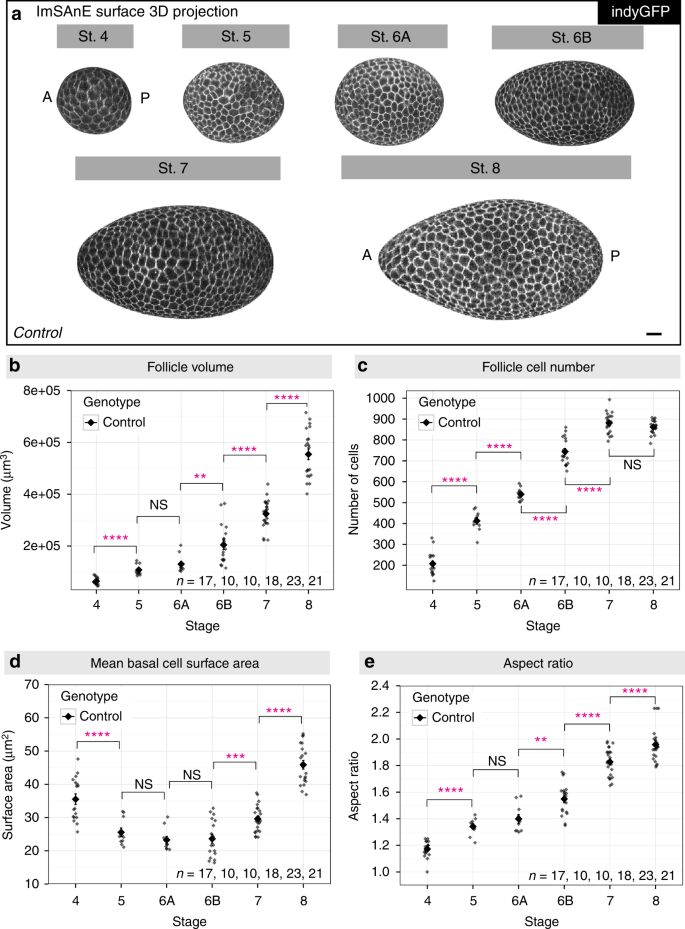
Extracellular matrix stiffness cues junctional remodeling for 3D tissue elongation
Recomendado para você
-
 Squishy literally gave me his old jersey at NARLI THIS is what makes him, and Rocket League so great. Go Cloud 9!!! : r/RocketLeague14 abril 2025
Squishy literally gave me his old jersey at NARLI THIS is what makes him, and Rocket League so great. Go Cloud 9!!! : r/RocketLeague14 abril 2025 -
 NACODEX Mini 60% Mechanical Gaming Keyboard - PBT Pudding Keycap Bluetooth 5.0 Rainbow Keyboard - 1000mAh Ultra-Compact Keyboard for Win/Mac/PC Gamer (Blue Switch Black) : Video Games14 abril 2025
NACODEX Mini 60% Mechanical Gaming Keyboard - PBT Pudding Keycap Bluetooth 5.0 Rainbow Keyboard - 1000mAh Ultra-Compact Keyboard for Win/Mac/PC Gamer (Blue Switch Black) : Video Games14 abril 2025 -
 Cartoon Decompression 3D Punky Animal Phone Case for Xiaomi Redmi 9T 9A 9C 9 8A 814 abril 2025
Cartoon Decompression 3D Punky Animal Phone Case for Xiaomi Redmi 9T 9A 9C 9 8A 814 abril 2025 -
 Making Squishy Circuits From COTS Playdough : 9 Steps (with Pictures) - Instructables14 abril 2025
Making Squishy Circuits From COTS Playdough : 9 Steps (with Pictures) - Instructables14 abril 2025 -
 Big Chic Novelty Keycaps Gaming Accessories Mechanical Keyboard Keycap Personality Design Cartoon Cherry MX Axis Anim Keycap (Single R4 Keys (KIT 1) : Electronics14 abril 2025
Big Chic Novelty Keycaps Gaming Accessories Mechanical Keyboard Keycap Personality Design Cartoon Cherry MX Axis Anim Keycap (Single R4 Keys (KIT 1) : Electronics14 abril 2025 -
:format(jpeg)/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/52104725/IMG_1128.0.0.jpeg) Best mechanical keyboards of 2016 - Polygon14 abril 2025
Best mechanical keyboards of 2016 - Polygon14 abril 2025 -
 Folding Keyboard, iClever Bluetooth Travel Keyboard, Sync Up to 3 Devices, Metal Build, USB-C Recharge, Portable Foldable Keyboard with Stand Holder for iPad, iPhone, Smartphone, Laptop and Tablet : Electronics14 abril 2025
Folding Keyboard, iClever Bluetooth Travel Keyboard, Sync Up to 3 Devices, Metal Build, USB-C Recharge, Portable Foldable Keyboard with Stand Holder for iPad, iPhone, Smartphone, Laptop and Tablet : Electronics14 abril 2025 -
 Moneybagg Yo - U Played (feat. Lil Baby) (Lyric Video)14 abril 2025
Moneybagg Yo - U Played (feat. Lil Baby) (Lyric Video)14 abril 2025 -
 squeesh yum® jiggly buddies 3-count, Five Below14 abril 2025
squeesh yum® jiggly buddies 3-count, Five Below14 abril 2025 -
kittycouch® (@KittyCouch) / X14 abril 2025
você pode gostar
-
 Desenho De Ilustração Em Vetor Arte Linha Um Cavalo Correndo Com Uma Vaqueira Cavalgando Isolada Fundo Branco PNG , Desenho De Cavalo, Desenho De Vaca, Desenho De Menina Imagem PNG e Vetor14 abril 2025
Desenho De Ilustração Em Vetor Arte Linha Um Cavalo Correndo Com Uma Vaqueira Cavalgando Isolada Fundo Branco PNG , Desenho De Cavalo, Desenho De Vaca, Desenho De Menina Imagem PNG e Vetor14 abril 2025 -
 Sonic Advance Collection, Sonic Fanon Wiki14 abril 2025
Sonic Advance Collection, Sonic Fanon Wiki14 abril 2025 -
.jpg) Demon's Souls' servers to be shut down May 31st, 2012; PC port of14 abril 2025
Demon's Souls' servers to be shut down May 31st, 2012; PC port of14 abril 2025 -
 Desenhos fofos e fáceis de fazer para desenhar e colorir14 abril 2025
Desenhos fofos e fáceis de fazer para desenhar e colorir14 abril 2025 -
 blue rainbow friends hugs retro - Blue Rainbow Friends - Sticker14 abril 2025
blue rainbow friends hugs retro - Blue Rainbow Friends - Sticker14 abril 2025 -
![AmiAmi [Character & Hobby Shop] [Bonus] BD Harem in the Labyrinth of Another World Blu-ray BOX First Vol. Limited Production Edition w/Roxanne -Lingerie Ver.- 1/7 Scale Figure(Released)](https://img.amiami.com/images/product/review/222/MED-DVD2-51924_01.jpg) AmiAmi [Character & Hobby Shop] [Bonus] BD Harem in the Labyrinth of Another World Blu-ray BOX First Vol. Limited Production Edition w/Roxanne -Lingerie Ver.- 1/7 Scale Figure(Released)14 abril 2025
AmiAmi [Character & Hobby Shop] [Bonus] BD Harem in the Labyrinth of Another World Blu-ray BOX First Vol. Limited Production Edition w/Roxanne -Lingerie Ver.- 1/7 Scale Figure(Released)14 abril 2025 -
 How To Turn On Developer Mode Discord14 abril 2025
How To Turn On Developer Mode Discord14 abril 2025 -
 AMA about Mad World! (All questions from event 8-12 to 8, and Dev answers) : r/madworld14 abril 2025
AMA about Mad World! (All questions from event 8-12 to 8, and Dev answers) : r/madworld14 abril 2025 -
Steam Workshop::Shao Kahn (Mortal Kombat)14 abril 2025
-
 CapCut_sonic exe i am god14 abril 2025
CapCut_sonic exe i am god14 abril 2025

