Radiological identification and analysis of soft tissue musculoskeletal calcifications, Insights into Imaging
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 11 abril 2025
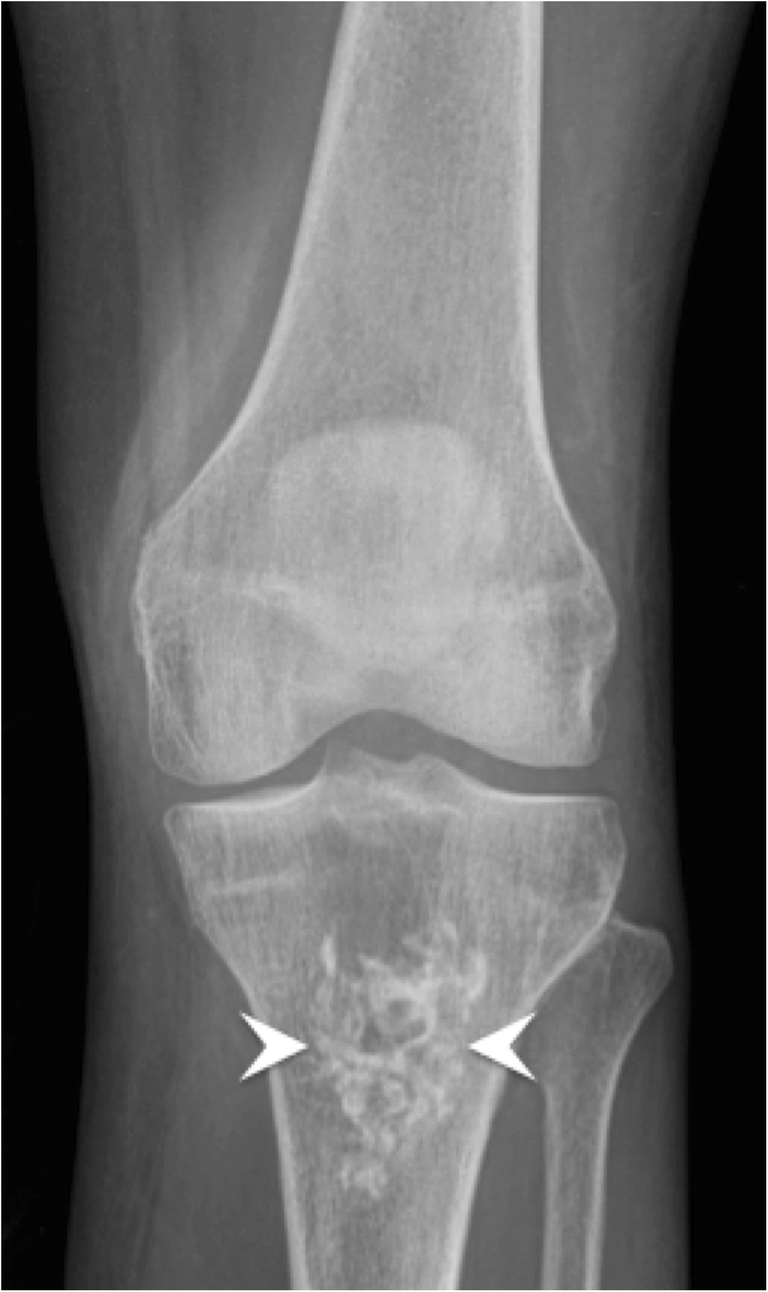
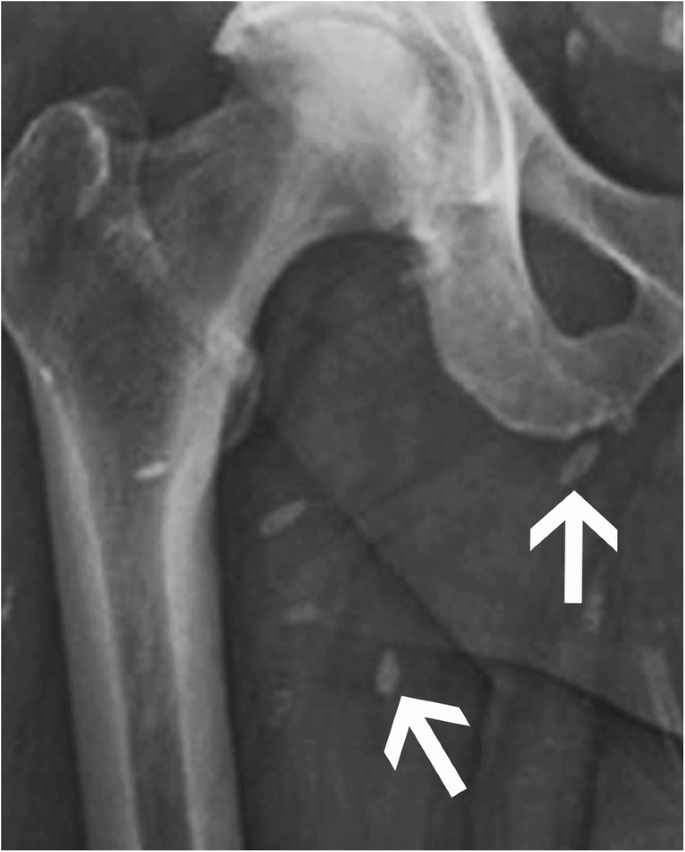
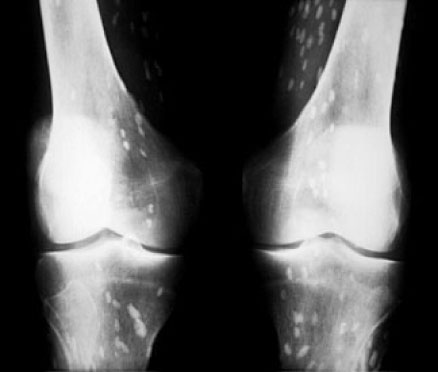
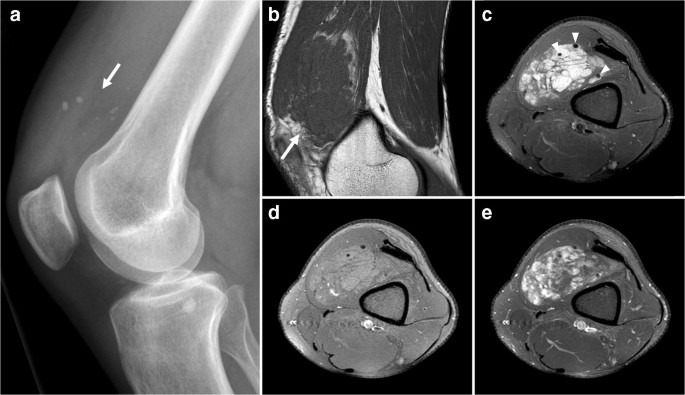
Abstract Musculoskeletal calcifications are frequent on radiographs and sometimes problematic. The goal of this article is to help radiologists to make the correct diagnosis when faced with an extraosseous musculoskeletal calcification. One should first differentiate a calcification from an ossification or a foreign body and then locate the calcification correctly. Each location has a specific short differential diagnosis, with minimal further investigation necessary. Intra-tendon calcifications are most frequently associated with hydroxyapatite deposition disease (HADD). In most cases, intra-articular calcifications are caused by calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate (CPPD) crystal deposition disease. Soft tissue calcification can be caused by secondary tumoural calcinosis from renal insufficiency, or collagen vascular diseases and by vascular calcifications, either arterial or venous (phlebolith). Teaching Points • Calcifications have to be differentiated form ossification and foreign body. • A musculoskeletal MRI study must always be correlated with a radiograph. • The clinical manifestations of calcifications may sometimes mimic septic arthritis or sarcoma. • HADD and CPPD crystal deposition have a distinct appearance on radiograph. • Calcinosis is more frequently caused by chronic renal failure and scleroderma.
Radiological identification and analysis of soft tissue musculoskeletal calcifications, Insights into Imaging
Soft Tissue Calcifications

State of the Art: Imaging of Osteoarthritis—Revisited 2020
Calcified or ossified benign soft tissue lesions that may simulate malignancy

Dermatomyositis presenting with diffuse calcinosis

Incidental findings in and around the prostate on prostate MRI: a pictorial review
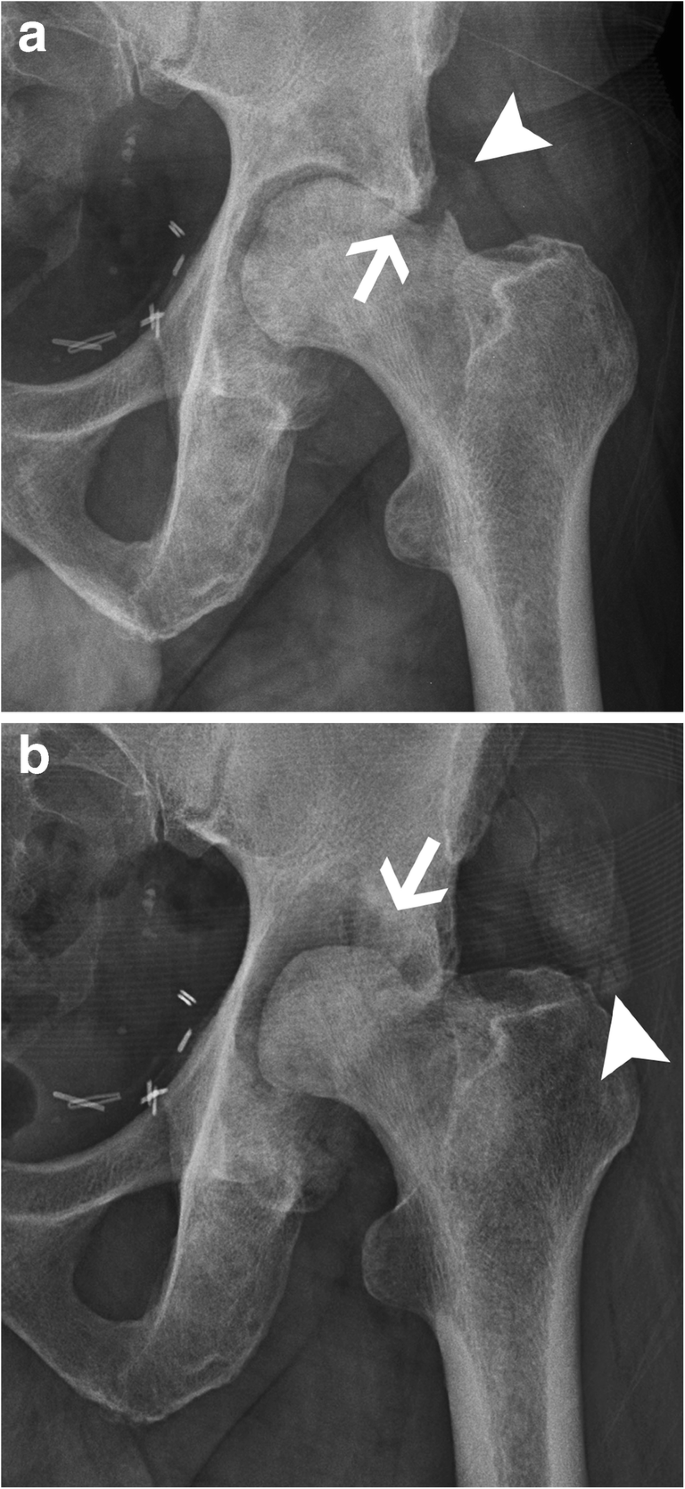
Radiological identification and analysis of soft tissue musculoskeletal calcifications, Insights into Imaging
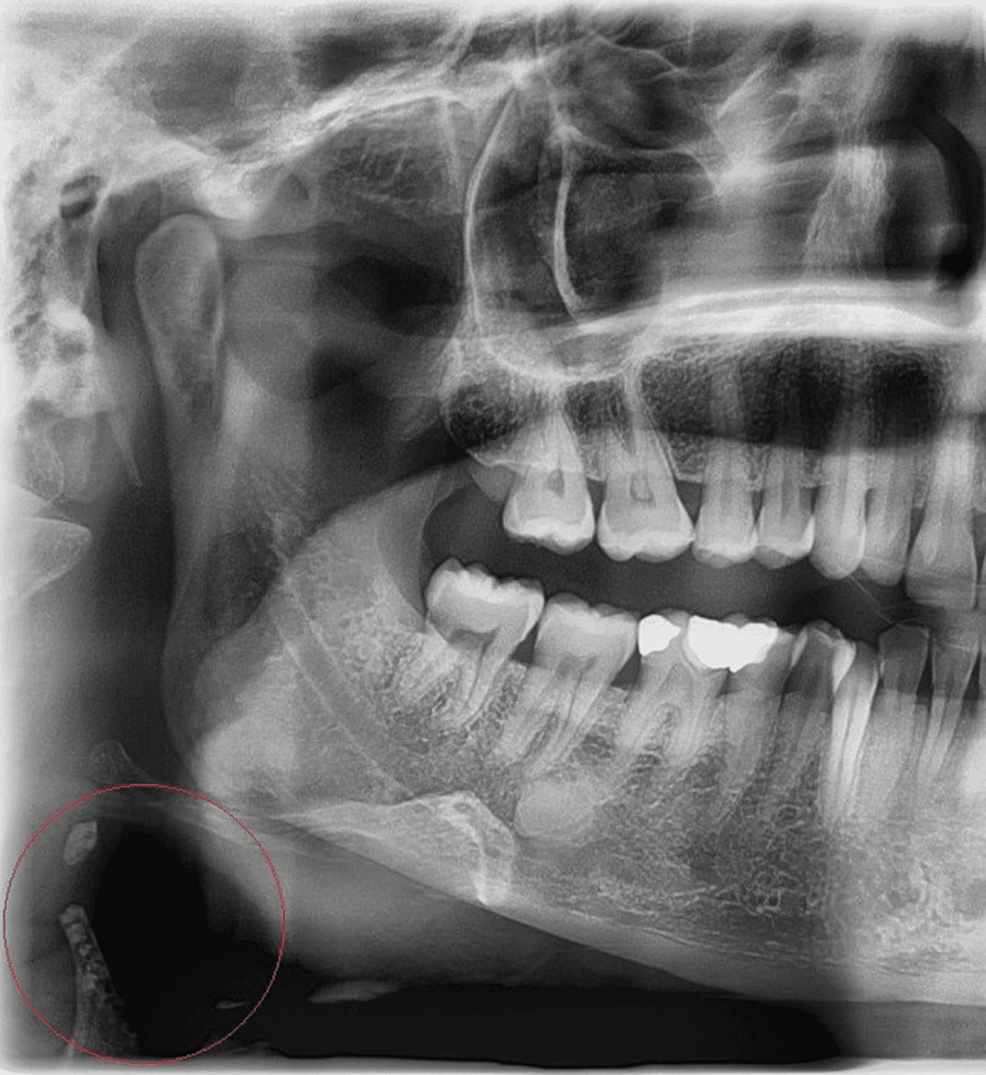
Cureus, Prevalence and Radiographic Features of Head and Neck Soft Tissue Calcifications on Digital Panoramic Radiographs: A Retrospective Study

Ultrasonography of Superficial Soft-Tissue Masses: Society of Radiologists in Ultrasound Consensus Conference Statement
Recomendado para você
-
 Ilizarov apparatus - Wikipedia11 abril 2025
Ilizarov apparatus - Wikipedia11 abril 2025 -
 TIBIA: KNIGHT RINGS FROM LEVEL 8 TO 220+ (SET EK)11 abril 2025
TIBIA: KNIGHT RINGS FROM LEVEL 8 TO 220+ (SET EK)11 abril 2025 -
 Ilizarov External Fixation System, Ilizarov External Fixation System Manufacturer, Ilizarov External Fixation System Suppliers, Orthopedic Implants, India11 abril 2025
Ilizarov External Fixation System, Ilizarov External Fixation System Manufacturer, Ilizarov External Fixation System Suppliers, Orthopedic Implants, India11 abril 2025 -
 tibia rings11 abril 2025
tibia rings11 abril 2025 -
 Might Ring, TibiaWiki11 abril 2025
Might Ring, TibiaWiki11 abril 2025 -
 SOLUTION: Img 20211217 wa0047 - Studypool11 abril 2025
SOLUTION: Img 20211217 wa0047 - Studypool11 abril 2025 -
 LORD OF THE RINGS & TWO TOWERS INTERPLAY +1Clk Windows 11 10 8 7 Vista – Allvideo Classic Games11 abril 2025
LORD OF THE RINGS & TWO TOWERS INTERPLAY +1Clk Windows 11 10 8 7 Vista – Allvideo Classic Games11 abril 2025 -
 Los Anillos de Poder: podría despedir a los showrunners debido a la recepción tibia de la serie11 abril 2025
Los Anillos de Poder: podría despedir a los showrunners debido a la recepción tibia de la serie11 abril 2025 -
 Medical Ring Fixator for Tibial & Femur Fracture in Orthopedic Tibia Industry - China Ilizarov, Ortopedi Ilizarov11 abril 2025
Medical Ring Fixator for Tibial & Femur Fracture in Orthopedic Tibia Industry - China Ilizarov, Ortopedi Ilizarov11 abril 2025 -
 Teen pregnancy affected dinosaurs too11 abril 2025
Teen pregnancy affected dinosaurs too11 abril 2025
você pode gostar
-
 Fairy Tail Review – Happy, can you go find Grays shirt?!11 abril 2025
Fairy Tail Review – Happy, can you go find Grays shirt?!11 abril 2025 -
 Standardised Packaging for Tobacco Products Review of11 abril 2025
Standardised Packaging for Tobacco Products Review of11 abril 2025 -
 Best Fruits Tier List (King Legacy)11 abril 2025
Best Fruits Tier List (King Legacy)11 abril 2025 -
 JOGOS DE TERROR GRÁTIS11 abril 2025
JOGOS DE TERROR GRÁTIS11 abril 2025 -
 Phantom World Colors by HYPERTARGET on DeviantArt11 abril 2025
Phantom World Colors by HYPERTARGET on DeviantArt11 abril 2025 -
 2023 edition Omega European Masters11 abril 2025
2023 edition Omega European Masters11 abril 2025 -
 Desapego Games - Free Fire (FF) > 😈 XIT IPA IPHONE ATUALIZADO 😈11 abril 2025
Desapego Games - Free Fire (FF) > 😈 XIT IPA IPHONE ATUALIZADO 😈11 abril 2025 -
 User Recreates 'Silent Hill 2' Opening Scene in 'Dreams' - Bloody Disgusting11 abril 2025
User Recreates 'Silent Hill 2' Opening Scene in 'Dreams' - Bloody Disgusting11 abril 2025 -
 Tell me something. How is it that someone is completely okay with11 abril 2025
Tell me something. How is it that someone is completely okay with11 abril 2025 -
 How to Prepare and Serve Cress -- Harvest to Table11 abril 2025
How to Prepare and Serve Cress -- Harvest to Table11 abril 2025