Identification of de novo EP300 and PLAU variants in a patient with Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome-related arterial vasculopathy and skeletal anomaly
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 19 abril 2025
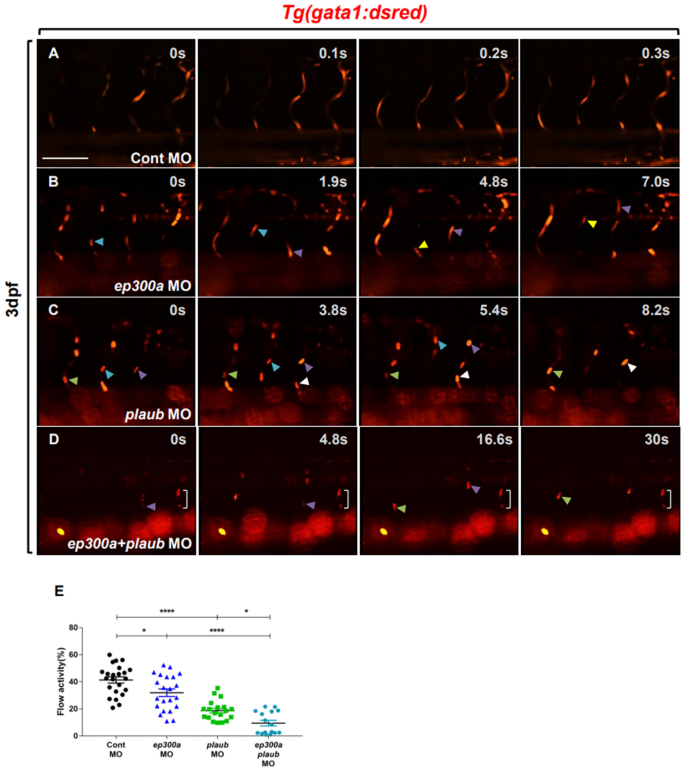
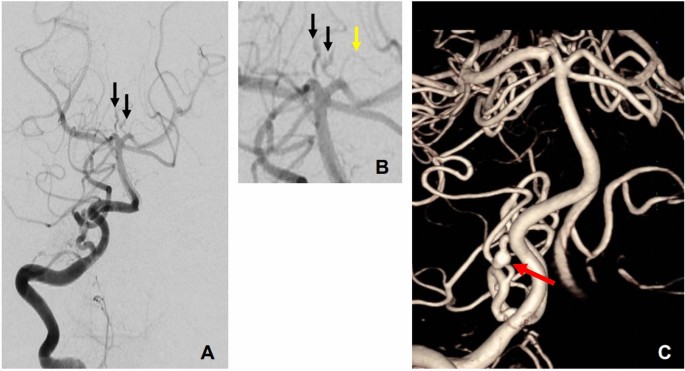
Identification of de novo EP300 and PLAU variants in a patient with Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome-related arterial vasculopathy and skeletal anomaly

Protein-protein interaction network describes the possible interaction

EP300‐related Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome: Highlighted rare phenotypic findings and a genotype–phenotype meta‐analysis of 74 patients - Cohen - 2020 - American Journal of Medical Genetics Part A - Wiley Online Library

Identification of 22q11.2 deletion in a patient with schizophrenia and clinically diagnosed Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome - Nagai - 2022 - Psychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences Reports - Wiley Online Library

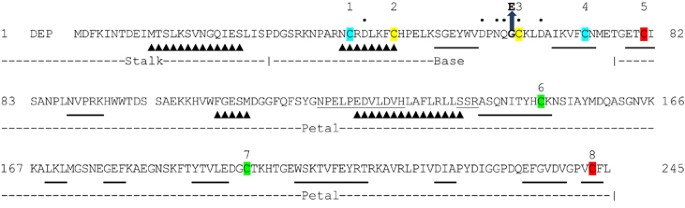
PDF) Persons with Quebec platelet disorder have a tandem duplication of PLAU, the urokinase plasminogen activator gene

Main clinical signs of the thirty-one Italian RSTS patients.

Substrate specificity of CBP. A , Western blot analysis of acetylation
Vascular Ehlers–Danlos Syndrome in siblings with biallelic COL3A1 sequence variants and marked clinical variability in the extended family
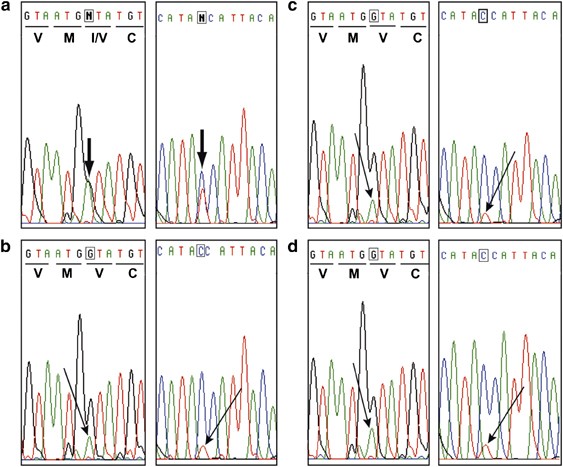
Segmental overgrowth, lipomatosis, arteriovenous malformation and epidermal nevus (SOLAMEN) syndrome is related to mosaic PTEN nullizygosity
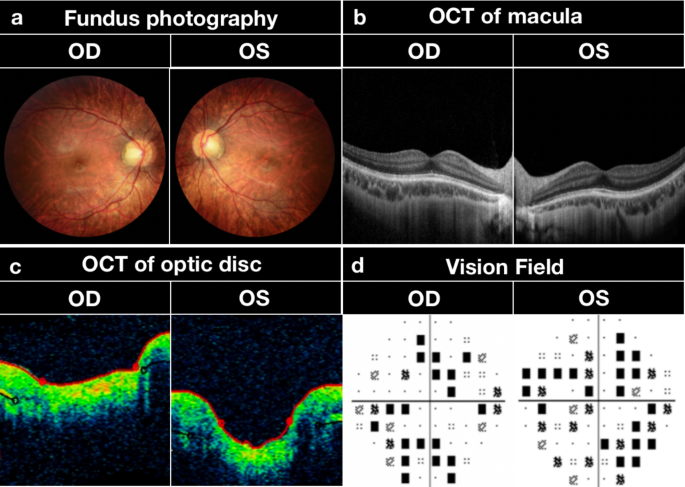
De novo variation in EP300 gene cause Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome 2 in a Chinese family with severe early-onset high myopia, BMC Medical Genomics
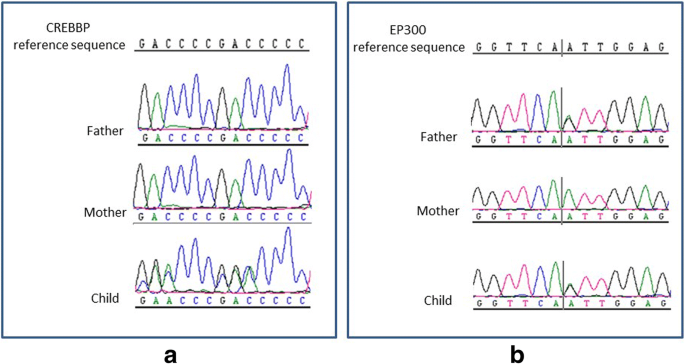
Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome in a Saudi boy with distinct features and variants in both the CREBBP and EP300 genes: a case report, BMC Medical Genetics
Recomendado para você
-
 Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome19 abril 2025
Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome19 abril 2025 -
 Born with Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome (RTS), Braxton and Family are19 abril 2025
Born with Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome (RTS), Braxton and Family are19 abril 2025 -
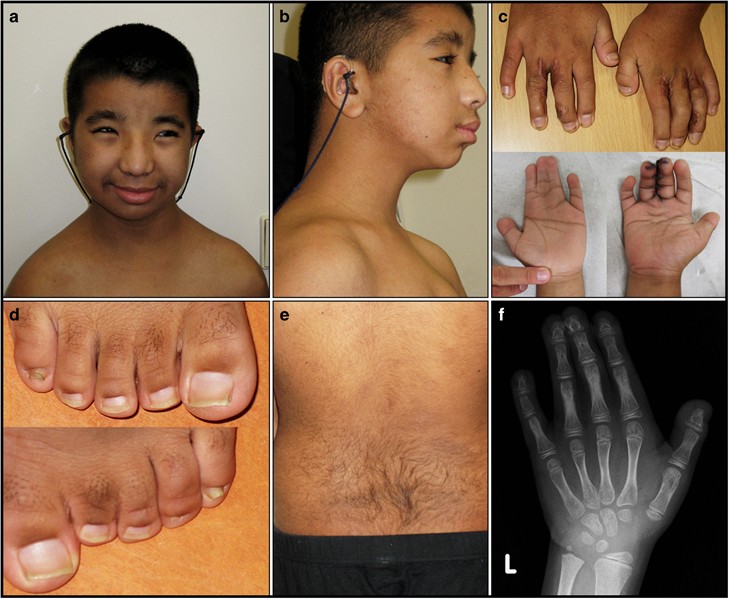
 Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome European Journal of Human Genetics19 abril 2025
Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome European Journal of Human Genetics19 abril 2025 -
 Rubinstein Syndrome - an overview19 abril 2025
Rubinstein Syndrome - an overview19 abril 2025 -
 Síndrome de Rubinstein-Taybi - Dra. Deborah Kerches19 abril 2025
Síndrome de Rubinstein-Taybi - Dra. Deborah Kerches19 abril 2025 -
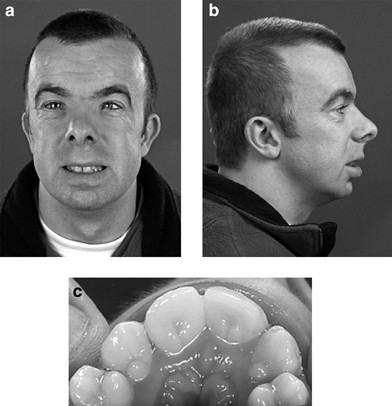
 Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome, medical and dental care for special needs patients: Clinical case report19 abril 2025
Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome, medical and dental care for special needs patients: Clinical case report19 abril 2025 -
Día Internacional del Síndrome de Rubinstein-Taybi - 3 de julio Asociación Española del Síndrome de Rubinstein-Taybi. (2020). 3 de julio - Día Internacional del Síndrome de Rubinstein-Taybi (SRT). 03/07/2020, de FEDER Sitio19 abril 2025
-
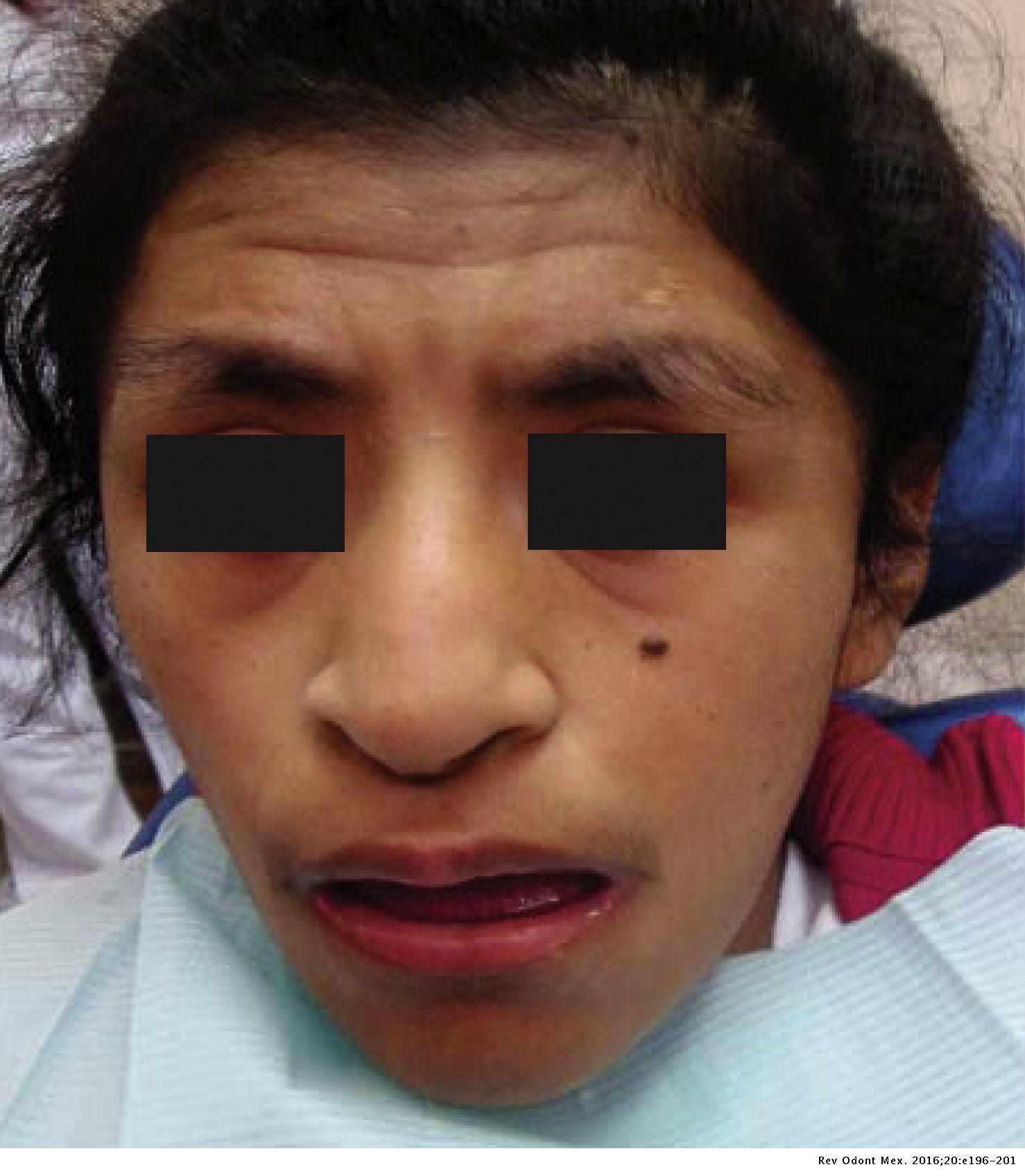
 Mosaic CREBBP mutation causes overlapping clinical features of19 abril 2025
Mosaic CREBBP mutation causes overlapping clinical features of19 abril 2025 -
 Molecular studies in 10 cases of Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome, including a mild variant showing a missense mutation in codon 1175 of CREBBP19 abril 2025
Molecular studies in 10 cases of Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome, including a mild variant showing a missense mutation in codon 1175 of CREBBP19 abril 2025 -
 Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome in diverse populations - Tekendo19 abril 2025
Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome in diverse populations - Tekendo19 abril 2025
você pode gostar
-
 Atriz portuguesa Daniela Melchior vai participar no “Velocidade19 abril 2025
Atriz portuguesa Daniela Melchior vai participar no “Velocidade19 abril 2025 -
Demon Slayer: Kimetsu no Yaiba - [ Demon Slayer: Kimetsu no Yaiba19 abril 2025
-
 Lille x PSG: onde assistir ao vivo e online, horário, escalação e mais do Campeonato Francês19 abril 2025
Lille x PSG: onde assistir ao vivo e online, horário, escalação e mais do Campeonato Francês19 abril 2025 -
 Guia N-Blast: The Legend of Zelda - A Link Between Worlds by Nintendo Blast - Issuu19 abril 2025
Guia N-Blast: The Legend of Zelda - A Link Between Worlds by Nintendo Blast - Issuu19 abril 2025 -
 Universal Studios Florida, Orlando, Florida, United States - Theme Park Review19 abril 2025
Universal Studios Florida, Orlando, Florida, United States - Theme Park Review19 abril 2025 -
Homem caindo de pára-quedas, Gráficos - Envato Elements19 abril 2025
-
 Novorizontino x Cruzeiro: onde assistir ao jogo pela Série B do Brasileirão - Superesportes19 abril 2025
Novorizontino x Cruzeiro: onde assistir ao jogo pela Série B do Brasileirão - Superesportes19 abril 2025 -
Road Safety in Vietnam Traffic accidents, crash, fatalities19 abril 2025
-
Download Instant Buttons The Best Soundboard App Free for Android - Instant Buttons The Best Soundboard App APK Download19 abril 2025
-
 ANAMNESE ADULTA COMPLETA Manuais, Projetos, Pesquisas Psicologia19 abril 2025
ANAMNESE ADULTA COMPLETA Manuais, Projetos, Pesquisas Psicologia19 abril 2025


