Staphylococcus Aureus Cells, Heat-Inactivated
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 12 abril 2025
Heat-killed Staphylococcus aureus cells in dextran solution. Antigen is intended for use as a positive control in immunoassay development for
Frontiers Staphylococcus aureus Infection Influences the Function of Intestinal Cells by Altering the Lipid Raft-Dependent Sorting of Sucrase–Isomaltase

Chronic Staphylococcus aureus infection is cured by theory-driven therapy
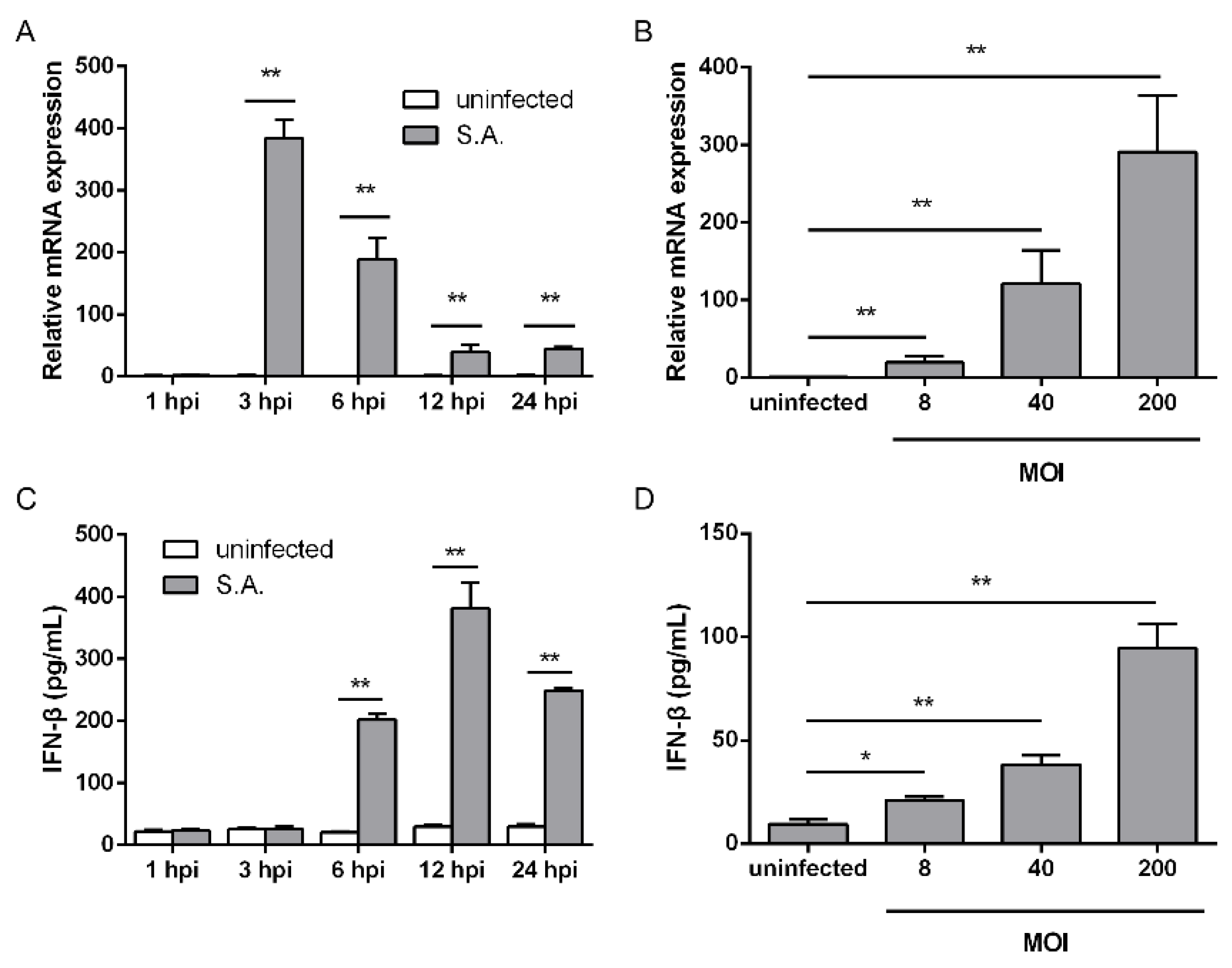
Pathogens, Free Full-Text
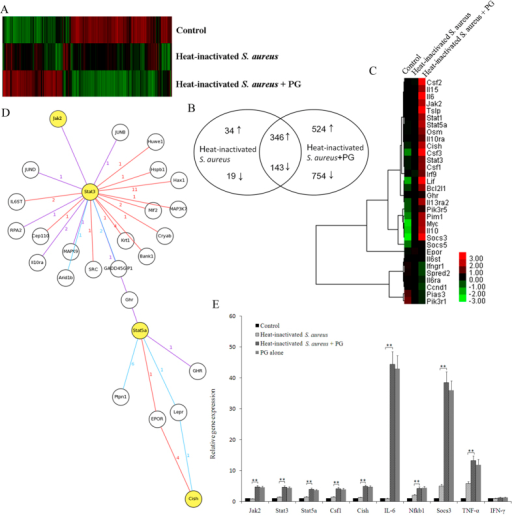
Analysis of signaling pathways required for the phagoso
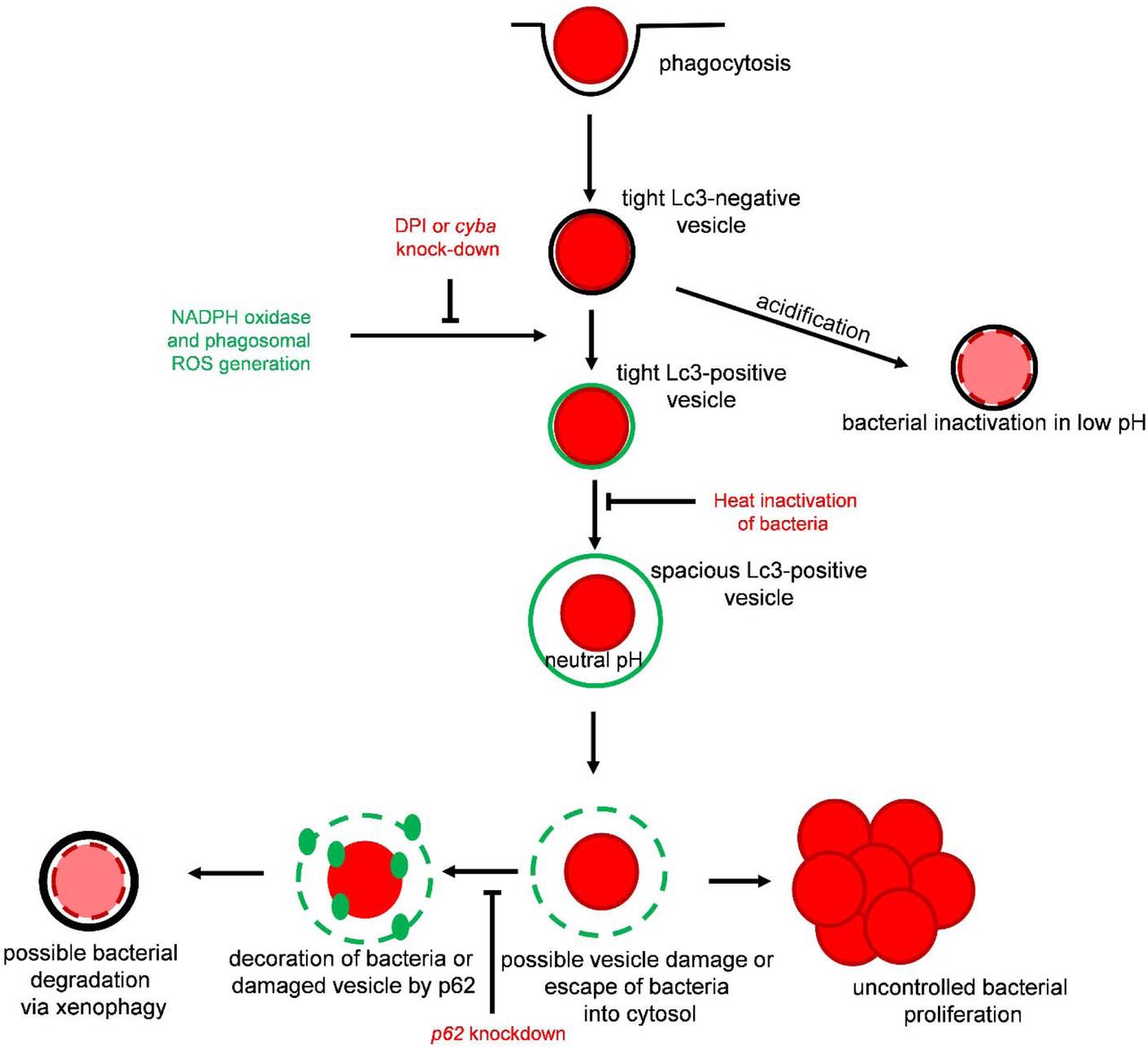
The autophagic response to Staphylococcus aureus provides an intracellular niche in neutrophils

A Metabolite of Pseudomonas Triggers Prophage-Selective Lysogenic to Lytic Conversion in Staphylococcus aureus

A Clinically Selected Staphylococcus aureus clpP Mutant Survives Daptomycin Treatment by Reducing Binding of the Antibiotic and Adapting a Rod-Shaped Morphology
Heat resistance, membrane fluidity and sublethal damage in Staphylococcus aureus cells grown at different temperatures - Repositorio Institucional de Documentos

Neutrophils Protect Against Staphylococcus aureus Endocarditis Progression Independent of Extracellular Trap Release
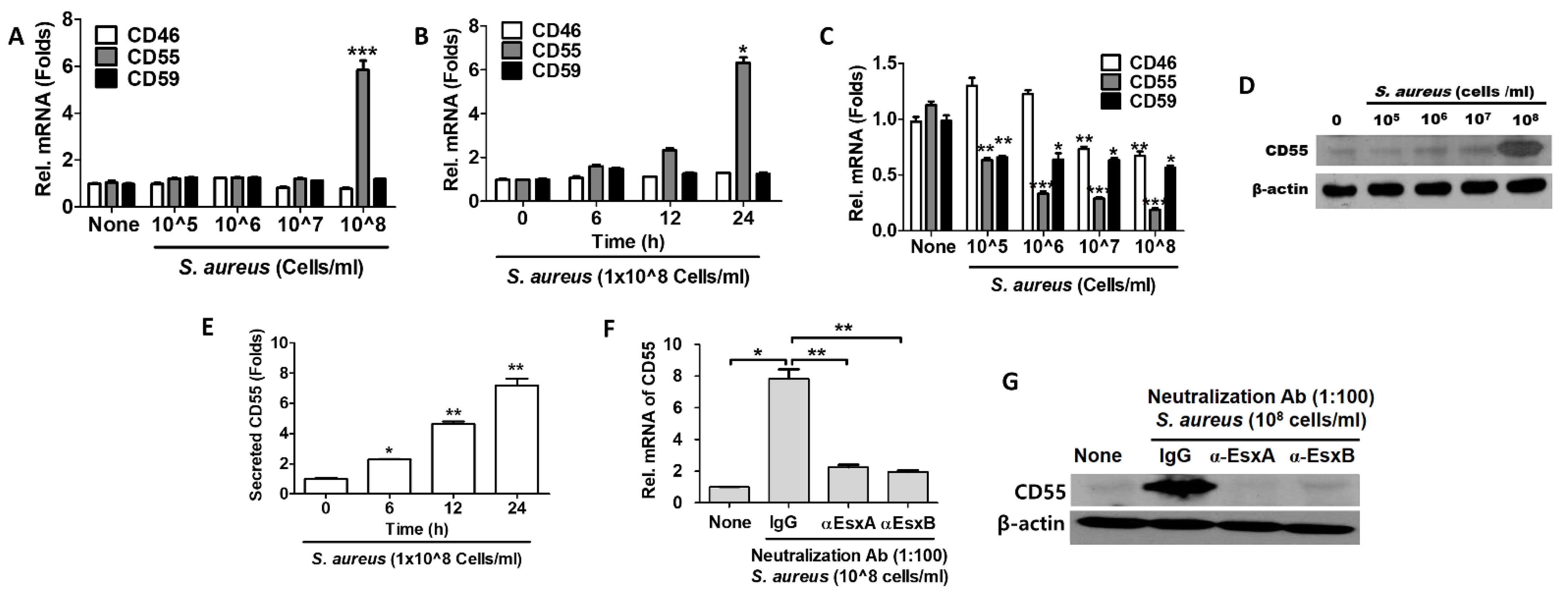
IJMS, Free Full-Text

Main Factors of Staphylococcus aureus Associated with the Interaction to the Cells for Their Colonization and Persistence
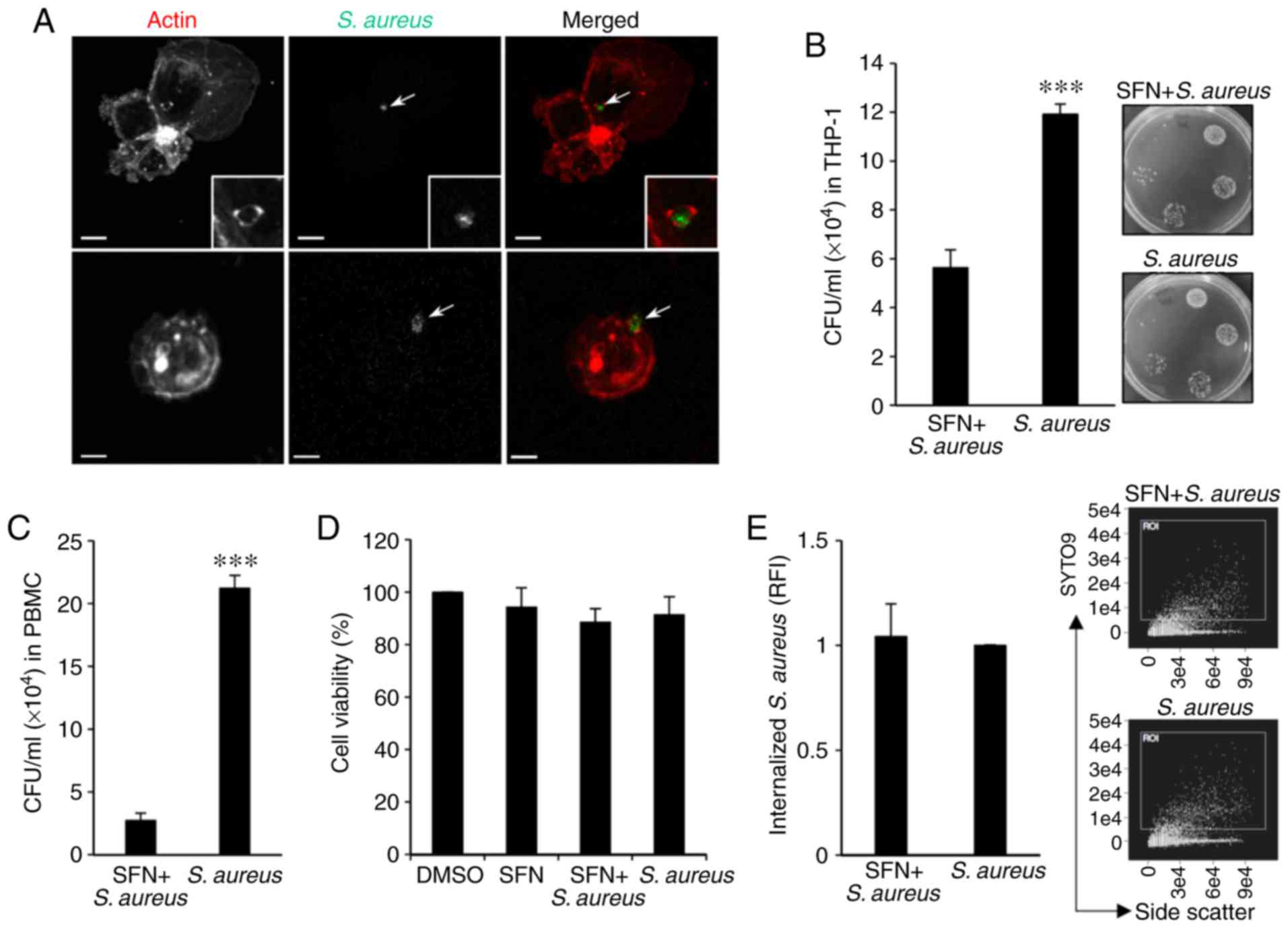
Sulforaphane reduces intracellular survival of Staphylococcus aureus in macrophages through inhibition of JNK and p38 MAPK‑induced inflammation
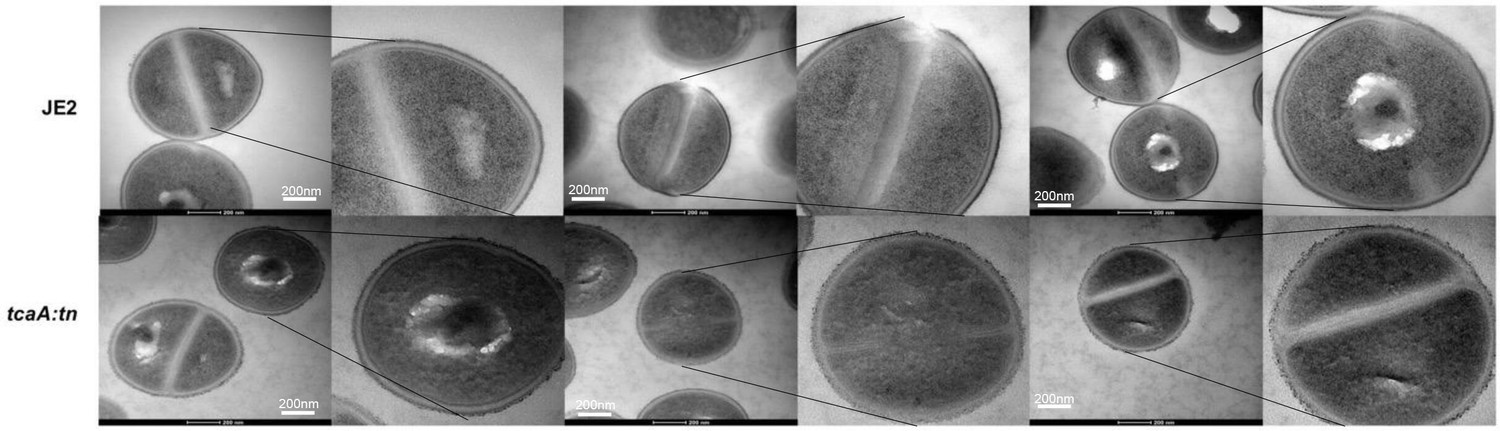
Extensive remodelling of the cell wall during the development of Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia

In vivo growth of Staphylococcus lugdunensis is facilitated by the concerted function of heme and non-heme iron acquisition mechanisms
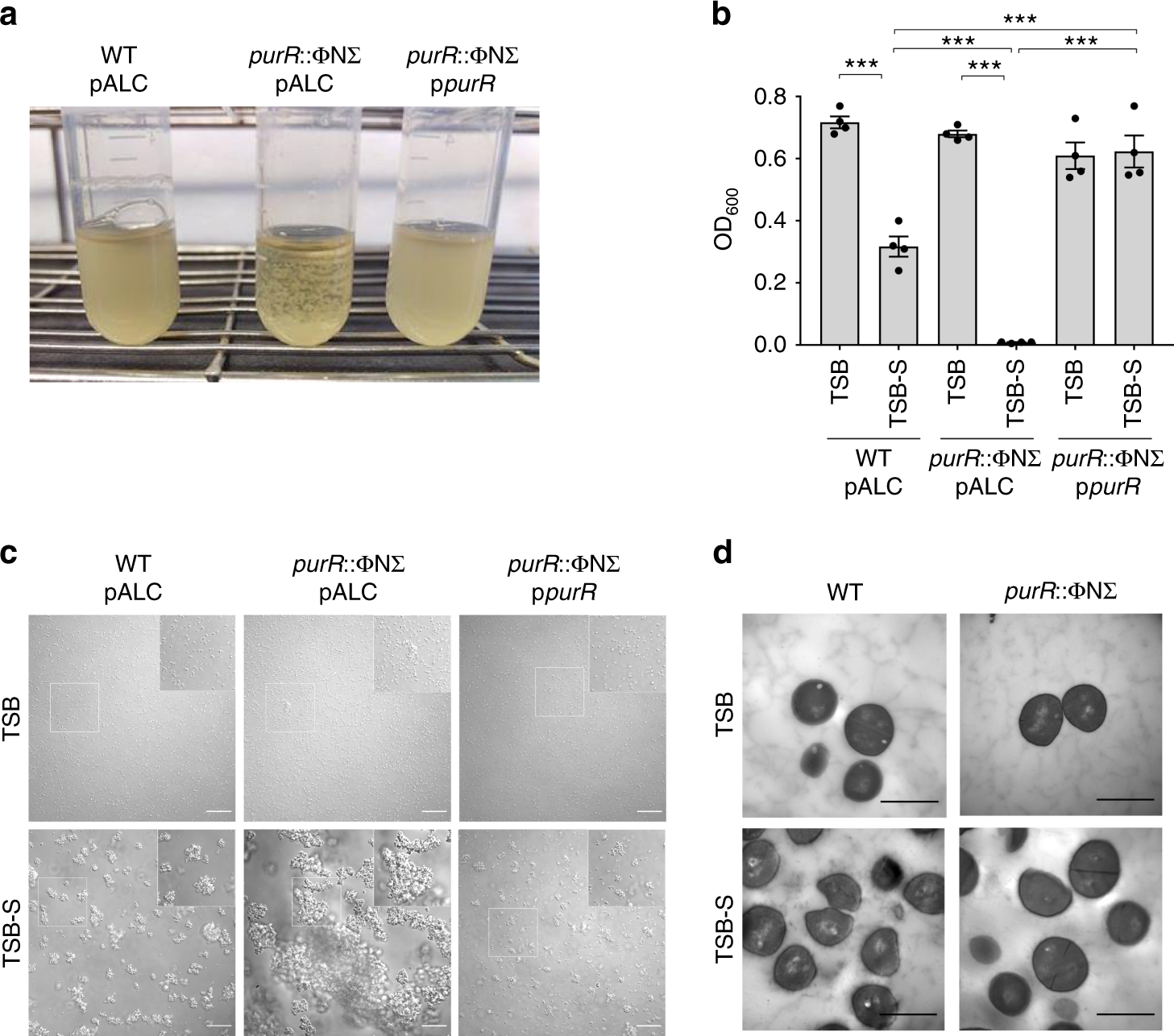
Stress-induced inactivation of the Staphylococcus aureus purine biosynthesis repressor leads to hypervirulence
Recomendado para você
-
 Staphylococcus - Wikipedia12 abril 2025
Staphylococcus - Wikipedia12 abril 2025 -
 Staphylococcus aureus: a new mechanism involved in virulence and antibiotic resistance - News from the Institut Pasteur12 abril 2025
Staphylococcus aureus: a new mechanism involved in virulence and antibiotic resistance - News from the Institut Pasteur12 abril 2025 -
 Staphylococcus Aureus: Transmission, Symptoms, Risk Factors, Diagnosis and Treatment12 abril 2025
Staphylococcus Aureus: Transmission, Symptoms, Risk Factors, Diagnosis and Treatment12 abril 2025 -
 Are teicoplanin-non-susceptible Staphylococcus epidermidis strains increasing?12 abril 2025
Are teicoplanin-non-susceptible Staphylococcus epidermidis strains increasing?12 abril 2025 -
 What Is a Staph Infection? - Causes, Symptoms & Treatments - Video & Lesson Transcript12 abril 2025
What Is a Staph Infection? - Causes, Symptoms & Treatments - Video & Lesson Transcript12 abril 2025 -
 Staphylococcal Infections: MedlinePlus12 abril 2025
Staphylococcal Infections: MedlinePlus12 abril 2025 -
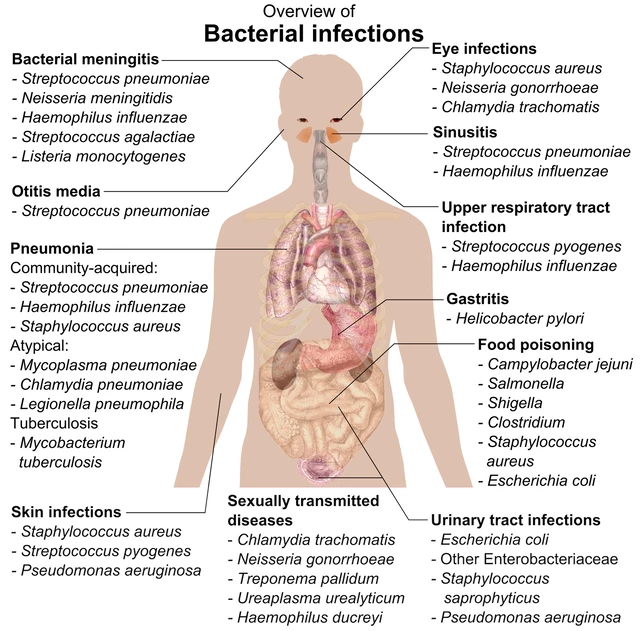 Staphylococcal Infections - StoryMD12 abril 2025
Staphylococcal Infections - StoryMD12 abril 2025 -
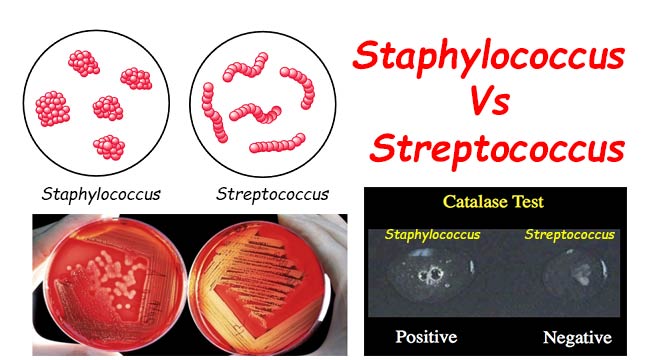 Differences Between Staphylococcus and Streptococcus - Microbiology Info.com12 abril 2025
Differences Between Staphylococcus and Streptococcus - Microbiology Info.com12 abril 2025 -
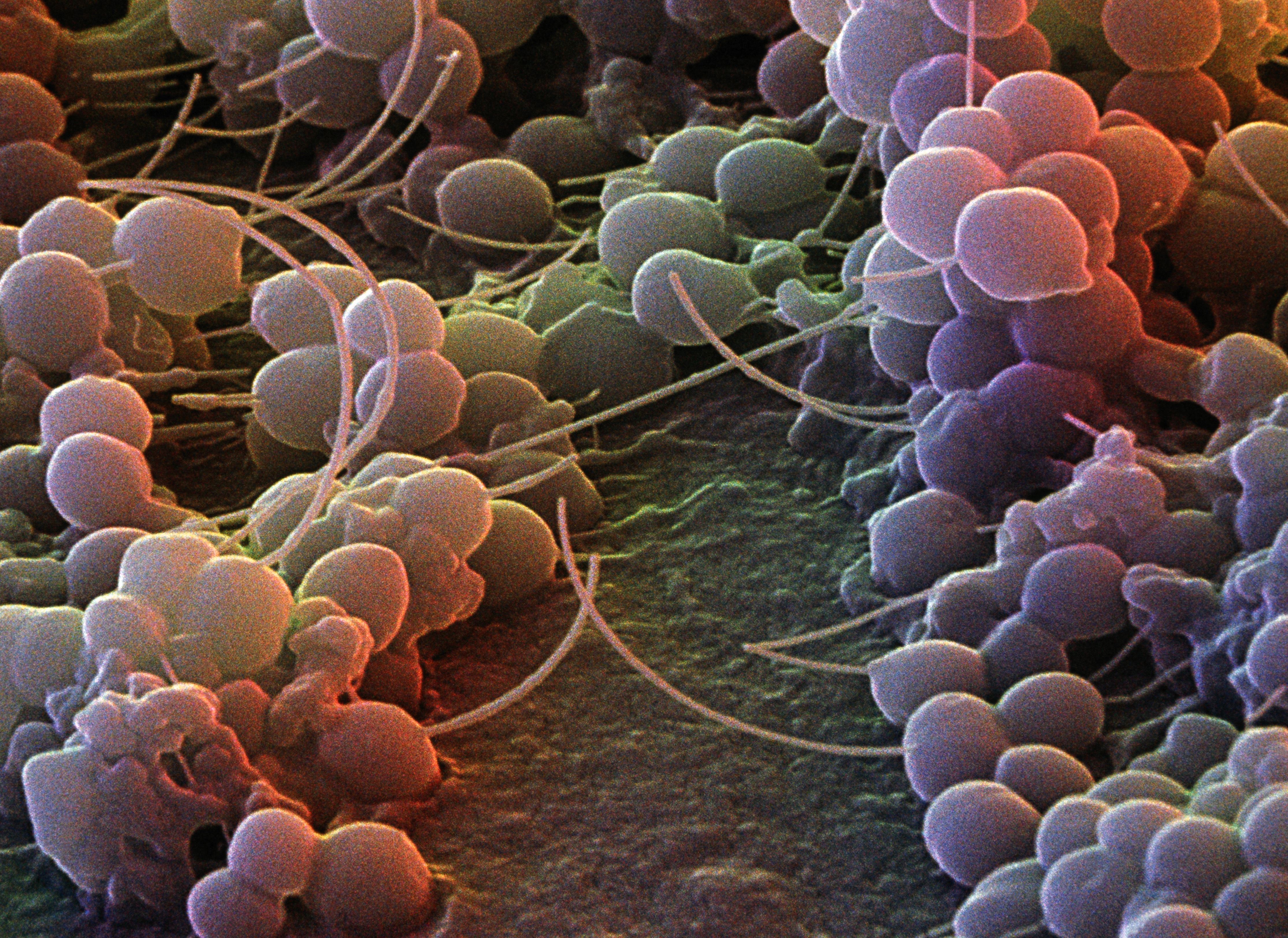 Microbiology from A to Z explained - Micropia - Micropia12 abril 2025
Microbiology from A to Z explained - Micropia - Micropia12 abril 2025 -
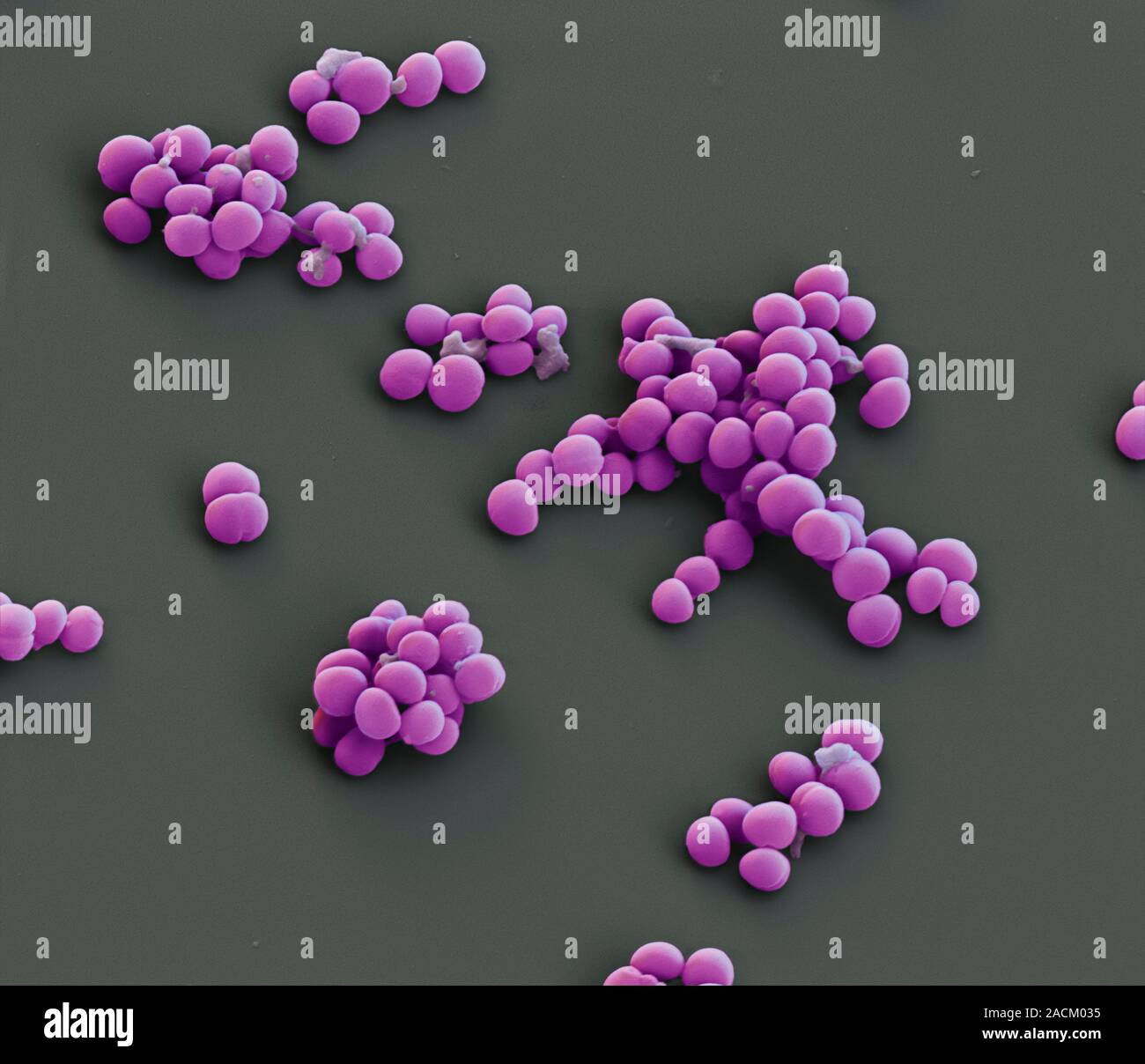 Staphylococcus pseudintermedius. Coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius bacteria. These Gram-positive cocci (s Stock Photo - Alamy12 abril 2025
Staphylococcus pseudintermedius. Coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius bacteria. These Gram-positive cocci (s Stock Photo - Alamy12 abril 2025
você pode gostar
-
 Genio Quiz - 4 - Wattpad12 abril 2025
Genio Quiz - 4 - Wattpad12 abril 2025 -
PC Game Pass on X: framing this #XboxShowcase / X12 abril 2025
-
![100+] Going Merry Wallpapers](https://wallpapers.com/images/hd/going-merry-1920-x-1080-wallpaper-pxsln2sl6m1aetkm.jpg) 100+] Going Merry Wallpapers12 abril 2025
100+] Going Merry Wallpapers12 abril 2025 -
 STL file Iori Yagami KOF 🎨・3D printer model to download・Cults12 abril 2025
STL file Iori Yagami KOF 🎨・3D printer model to download・Cults12 abril 2025 -
Codblox - Promo Codes - Apps on Google Play12 abril 2025
-
PlayStation anuncia evento State of Play para esta quinta-feira (14)12 abril 2025
-
 Zilu é humilhada por Zezé, se vinga e ele diz o porquê casou: Onde12 abril 2025
Zilu é humilhada por Zezé, se vinga e ele diz o porquê casou: Onde12 abril 2025 -
 Brasil Gaming House - Liquipedia Overwatch Wiki12 abril 2025
Brasil Gaming House - Liquipedia Overwatch Wiki12 abril 2025 -
 Batman logo, Batman sign, Logo, Dark, 4K, HD wallpaper12 abril 2025
Batman logo, Batman sign, Logo, Dark, 4K, HD wallpaper12 abril 2025 -
 STUDIO WILDCARD REVEALS FIRST TRAILER & GAMEPLAY DETAILS FOR ITS12 abril 2025
STUDIO WILDCARD REVEALS FIRST TRAILER & GAMEPLAY DETAILS FOR ITS12 abril 2025
