Polymers, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 19 março 2025

An ecological mortar is designed from industrial sub-products, with the objective of utilizing both the slag residues, generated during steel manufacturing processes, and the waste from Polyurethane Foam (PF) panels, generated during refrigerator chamber manufacturing processes. The ecological mortar design involves the dosing of Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) slag, together with finely ground Polyurethane Foam, cement, and additives. An energy efficient prefabricated block is designed with the mortar, for use in construction, and its energy performance is assessed as a material inserted within the envelope of a service sector (hospital) building, either as an exterior skin, or as an enclosing component within the façade interior. The main contribution of this research is the characterization of the thermo-physical and mechanical properties of a new prefabricated panel made with recycled materials. The full characterization of the properties of these new materials is presented and discussed. The new prefabricated panel demonstrates adequate thermo-mechanical characteristics as a substitute for traditional materials, while improving the sustainability of the building. As a secondary objective, the energy behaviour of the new panels when integrated in a real building is presented by means of a case study simulation. The use of computational thermal simulation confirmed that the properties of the prefabricated block influenced the annual thermal demand of the building for heating and cooling. Improvements to the thermal inertia of the building envelope were also confirmed with the inclusion of PF waste, giving the mortar an energy performance that was similar to conventional materials, in such a way that its use in façade construction may be validated, in addition to its environmental benefits, due to it having been manufactured with critical recycled industrial waste such as EAF slag and PF, thereby contributing to both the circular economy and sustainable development.
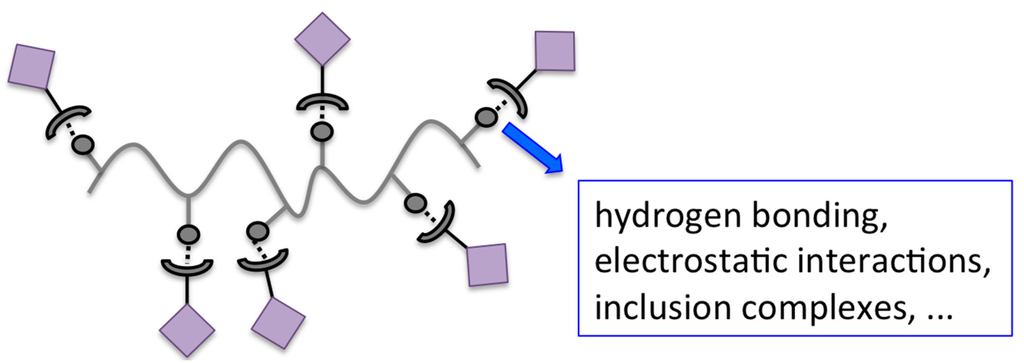
Polymers, Free Full-Text
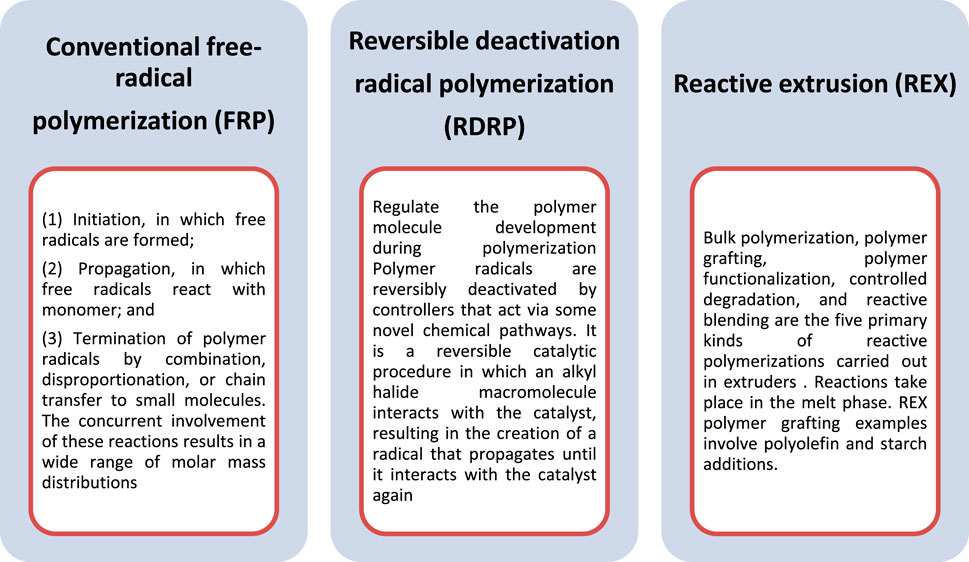
Frontiers Polymer Grafting and its chemical reactions

Filled Polymers: Science and Industrial Applications - 1st Edition - J

Free-radical polymerization of 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate (HEMA) supported by a high electric field - Polymer Chemistry (RSC Publishing)
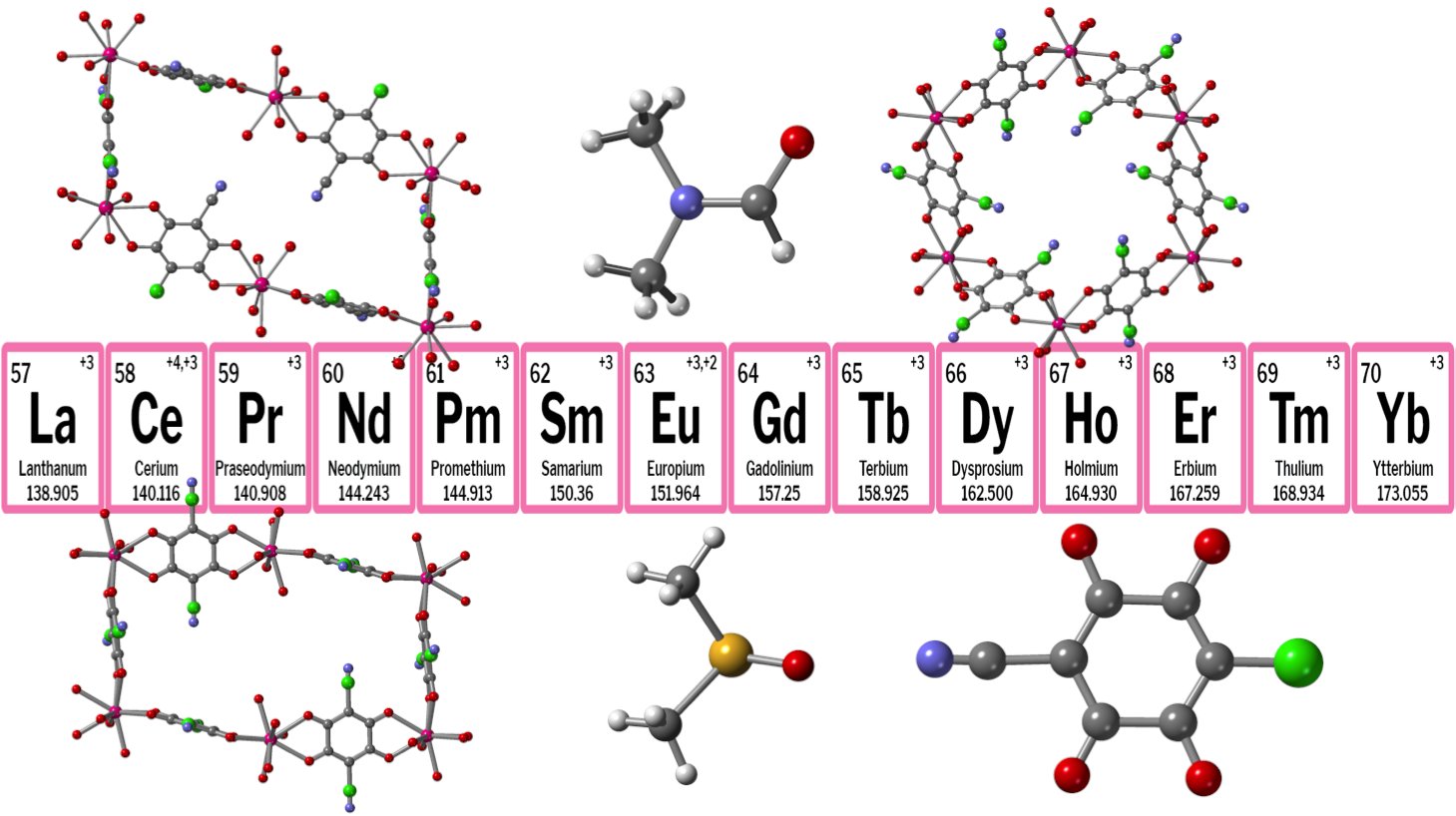
Magnetochemistry MDPI on X: #HighlyAccessedPaper #HighlyCitedPaper #Magnetochemistry Two Dimensional Magnetic Coordination Polymers Formed by Lanthanoids and Chlorocyananilato Free full-text is available at: Welcome to read

Solvent‐Free Chemical Recycling of Polymethacrylates made by ATRP and RAFT polymerization: High‐Yielding Depolymerization at Low Temperatures - Whitfield - 2023 - Angewandte Chemie International Edition - Wiley Online Library
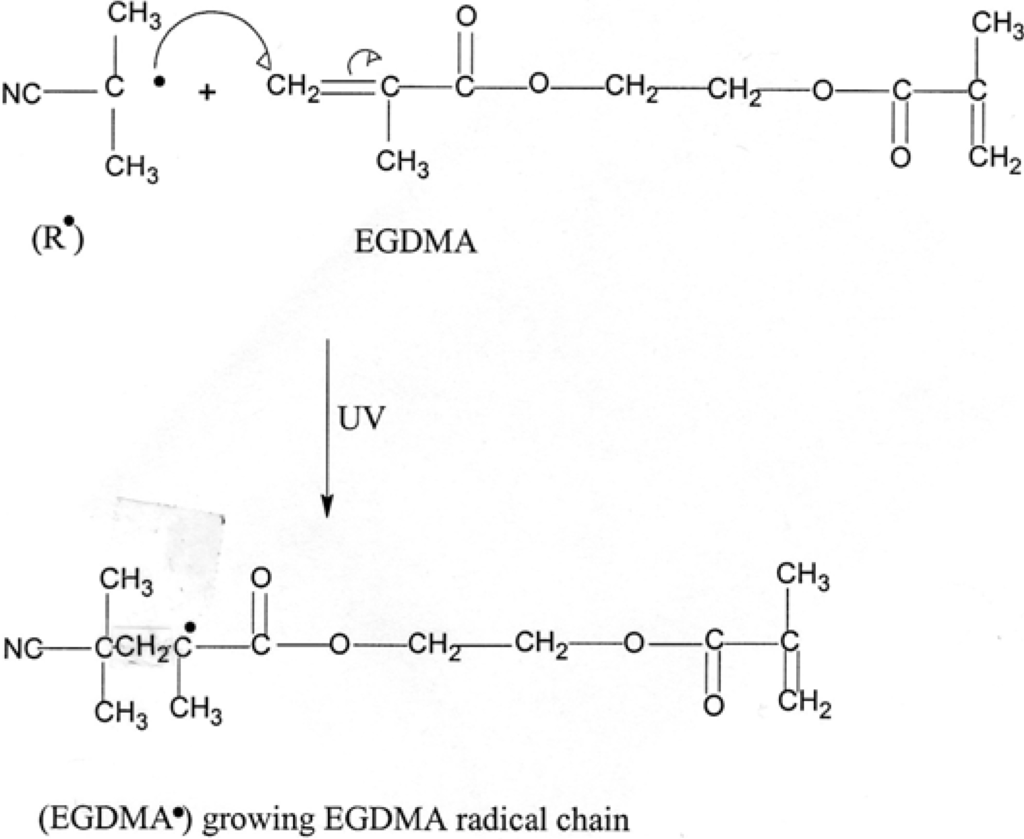
Polymers Free Full-Text Synthesis Of Ethylene Glycol Dimethacrylate-Methyl Methacrylate Copolymers, Determination Of Their Reactivity Ratios, And A Study Of Dopant And Temperature Effects On Their Conductivities

Polymer animated word cloud, text design, Stock Video

Reversing RAFT Polymerization: Near-Quantitative Monomer Generation Via a Catalyst-Free Depolymerization Approach

Dielectric Properties of Polymers - Materials Square
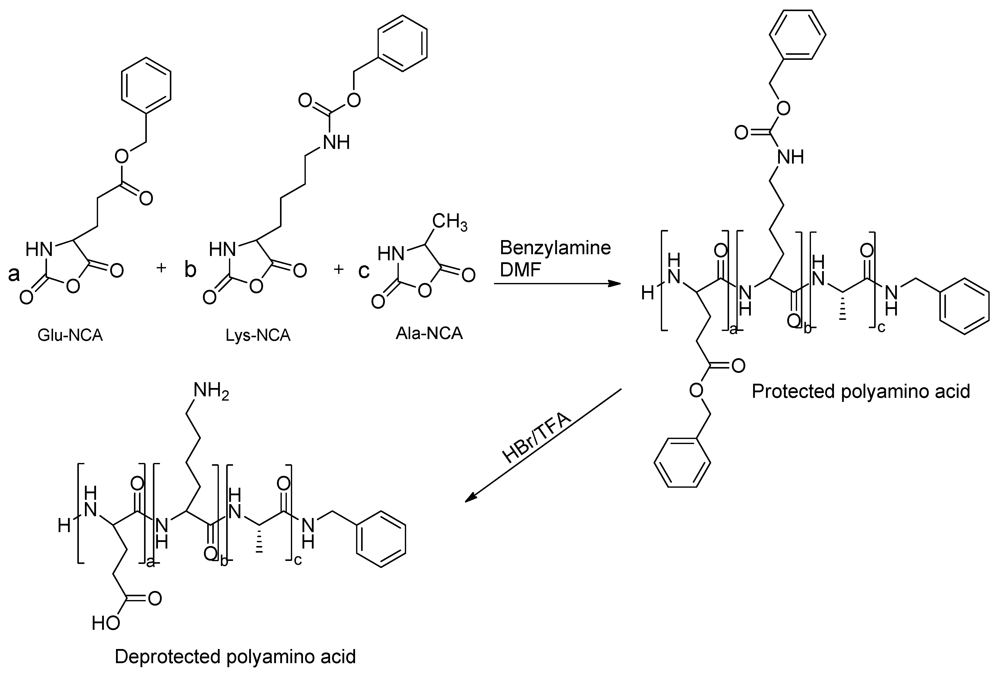
Polymers, Free Full-Text

Solvent-free synthesis of N-containing polymers with high cross-linking degree to generate N-doped porous carbons for high-efficiency CO2 capture - ScienceDirect
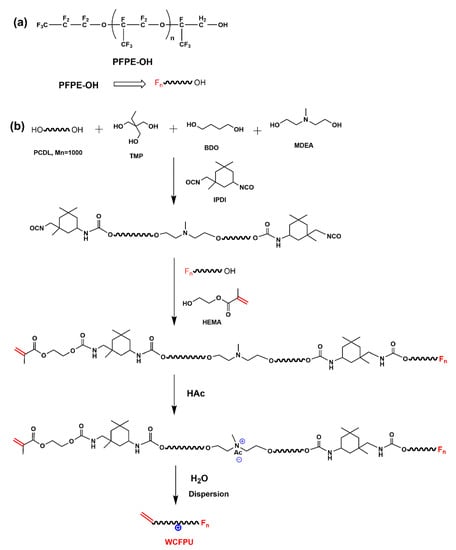
Download Software Predict Voc Emissions Polymers - Colaboratory
Recomendado para você
-
 Roblox - Blox Fruits - Lista de códigos e como resgatá-los19 março 2025
Roblox - Blox Fruits - Lista de códigos e como resgatá-los19 março 2025 -
 Códigos Blox Fruits Novembro 2023: como resgatar no Roblox19 março 2025
Códigos Blox Fruits Novembro 2023: como resgatar no Roblox19 março 2025 -
Code For Project Baki 219 março 2025
-
 todos os códigos de Double XP no Block Studio em 202319 março 2025
todos os códigos de Double XP no Block Studio em 202319 março 2025 -
 Macrovital19 março 2025
Macrovital19 março 2025 -
 Dragon Ball Rage codes – free zenkai, XP, and stats19 março 2025
Dragon Ball Rage codes – free zenkai, XP, and stats19 março 2025 -
Planilha Novo Template Importacao19 março 2025
-
 DPS - Digital Products Shop19 março 2025
DPS - Digital Products Shop19 março 2025 -
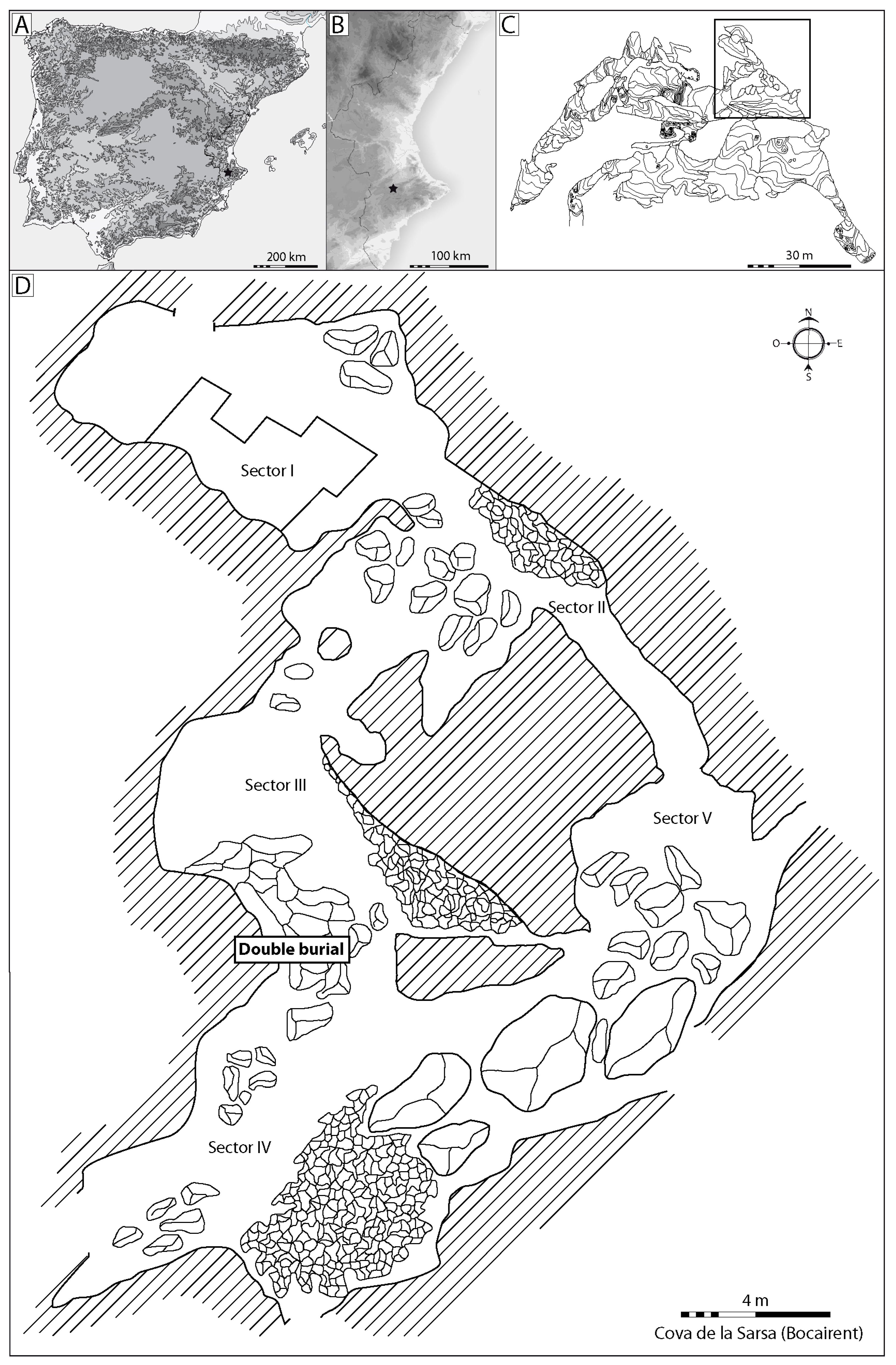 Heritage, Free Full-Text19 março 2025
Heritage, Free Full-Text19 março 2025 -
 Tourist Visas: How to Extend a Tourist Visa in Medellín – 2023 Update19 março 2025
Tourist Visas: How to Extend a Tourist Visa in Medellín – 2023 Update19 março 2025
você pode gostar
-
 Baixe o Bubble Shooter: Jogo de Bola MOD APK v3.421 para Android19 março 2025
Baixe o Bubble Shooter: Jogo de Bola MOD APK v3.421 para Android19 março 2025 -
 Guilty Gear Strive Bridget Combo Guide19 março 2025
Guilty Gear Strive Bridget Combo Guide19 março 2025 -
 Fireboy and Watergirl: Online in the Forest Temple Level 1-319 março 2025
Fireboy and Watergirl: Online in the Forest Temple Level 1-319 março 2025 -
 Amigo, Amigo's Pizzeria - Magill, Pizza & Pasta19 março 2025
Amigo, Amigo's Pizzeria - Magill, Pizza & Pasta19 março 2025 -
 A história de Killzone 2 - Enredo com spoilers19 março 2025
A história de Killzone 2 - Enredo com spoilers19 março 2025 -
 Our Office Story - Chapter 21 - Mangatx19 março 2025
Our Office Story - Chapter 21 - Mangatx19 março 2025 -
 Chrome division hi-res stock photography and images - Alamy19 março 2025
Chrome division hi-res stock photography and images - Alamy19 março 2025 -
 Rainbow Friends Inspired 5 Pc Fondant Cake Topper Set19 março 2025
Rainbow Friends Inspired 5 Pc Fondant Cake Topper Set19 março 2025 -
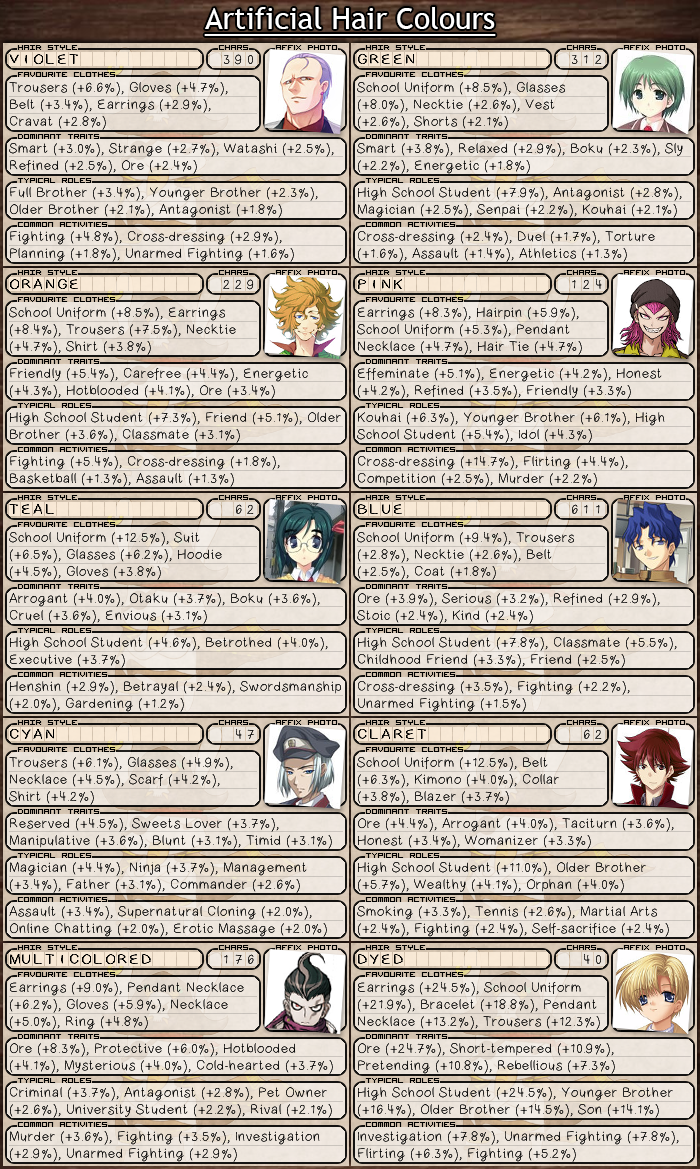 The Bunny Advocate — Hair Tropes in Japanese Media19 março 2025
The Bunny Advocate — Hair Tropes in Japanese Media19 março 2025 -
 Charizard ex sv3pt5 6 Pokemon TCG POK Cards19 março 2025
Charizard ex sv3pt5 6 Pokemon TCG POK Cards19 março 2025
