Pathogens, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 26 março 2025
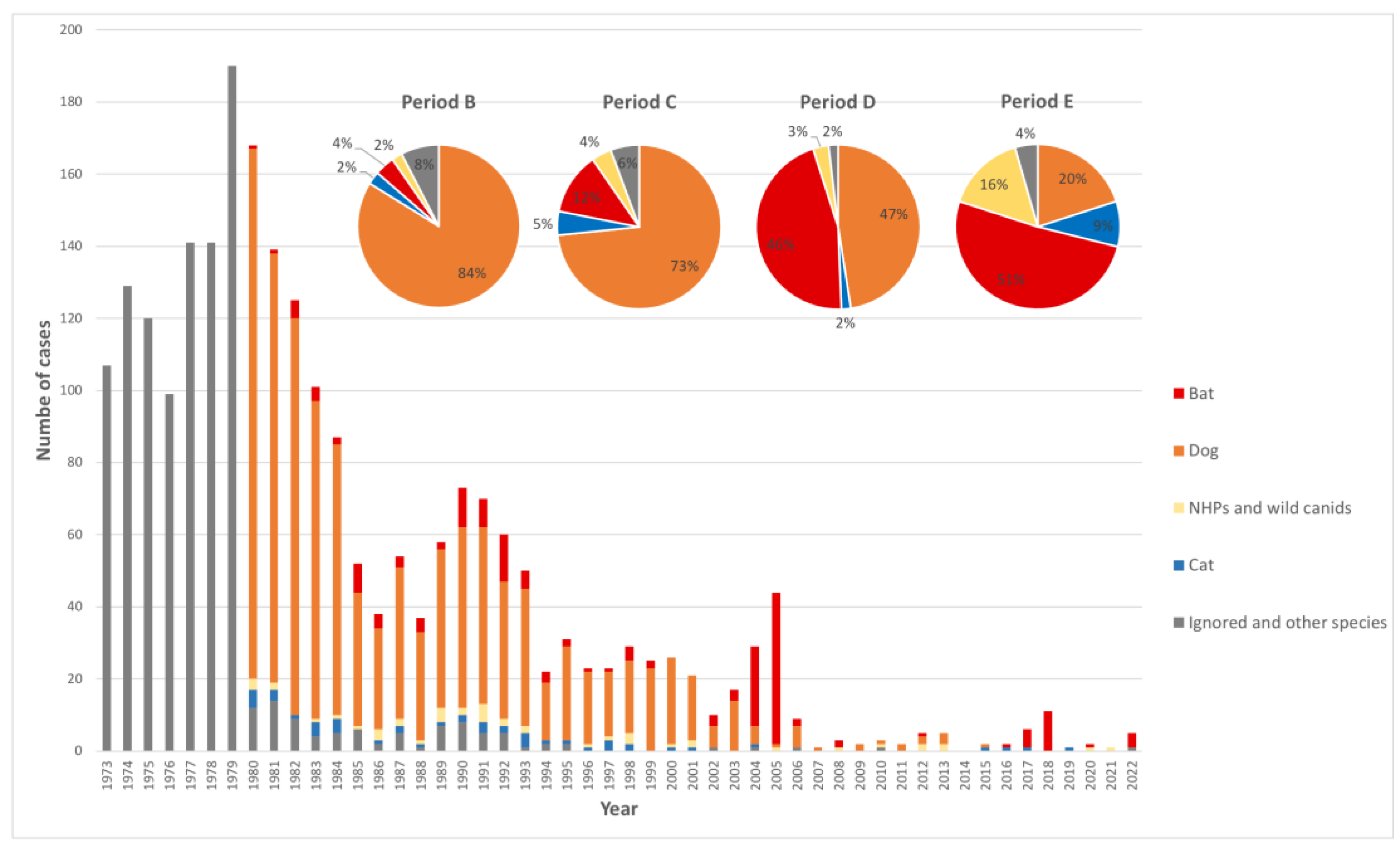
In 1973, the National Rabies Program was created in Brazil through an agreement between the Ministry of Health and Agriculture. Since its beginning, it developed integrated action through access to free post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) for people at risk, dog vaccination campaigns, a joint surveillance system, and awareness. This study aims to describe human rabies in Brazil under the One Health perspective in recent decades, including achievements in the control of dog-mediated cases and challenges in human cases transmitted by wild animals. This paper also explores possible drivers of human rabies in the Northeast Region with half of the cases. The first part of this study was descriptive, presenting data and examples by periods. Statistical analysis was performed in the last period (2010–2022) to explore possible drivers. Dog-mediated human cases decreased from 147 to 0, and dog cases decreased from 4500 to 7. A major challenge is now human cases transmitted by wild animals (bats, non-human primates, and wild canids). Most current human cases occur in municipalities with a tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forest biome and a Gini index higher than 0.5. In the multivariable analysis, an association with temperature was estimated (OR = 1.739; CI95% = 1.181–2.744), and primary healthcare coverage (OR = 0.947; CI95% = 0.915–0.987) was identified as a protector. It is possible to significantly reduce the number of dog-mediated human rabies cases through the efforts presented. However, Brazil has wildlife variants of the rabies virus circulating. The association of human cases with higher temperatures in the Northeast is a concern with climate change. To reduce human cases transmitted by wild animals, it is important to continue distributing free PEP, especially in remote at-risk areas in the Region, and to increase awareness.

Bloodborne Pathogens Handouts, First Aid
Pathogens An Open Access Journal from MDPI
Frontiers Identification and Control of Latent Bacteria in in vitro Cultures of Sweetpotato [Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam]
Figure 3 PLOS Pathogens
Pathogens, Free Full-Text

Sequential Infection with Common Pathogens Promotes Human-like Immune Gene Expression and Altered Vaccine Response - ScienceDirect

Pathogenic bacteria - Wikipedia
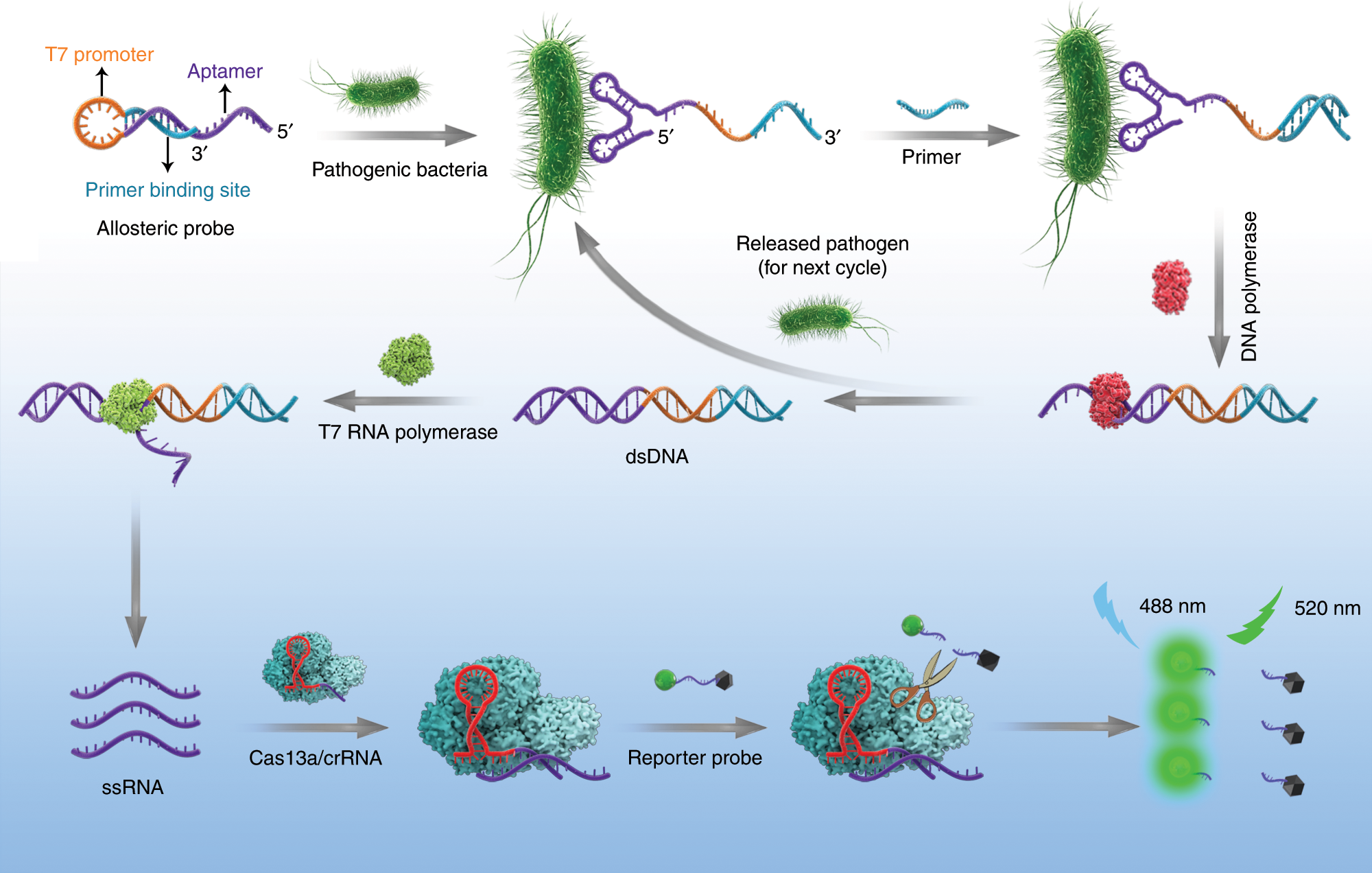
Sensitive detection of a bacterial pathogen using allosteric probe-initiated catalysis and CRISPR-Cas13a amplification reaction

Southeastern Naturalist, Volume 15, Number 1 (2016): N4–N6
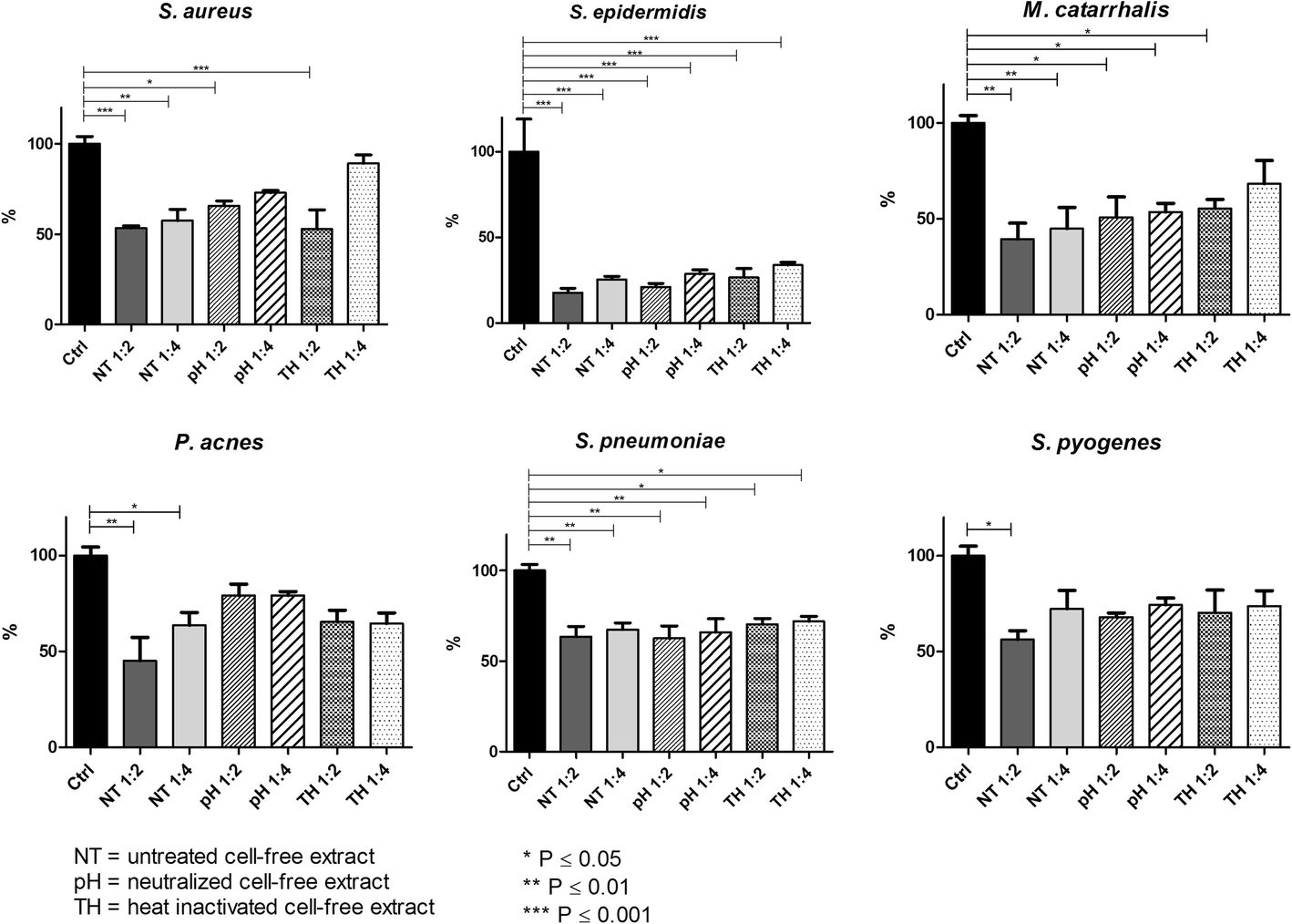
Probiotics Streptococcus salivarius 24SMB and Streptococcus oralis 89a interfere with biofilm formation of pathogens of the upper respiratory tract, BMC Infectious Diseases

Pathogenic Bacteria, Overview, Types & Examples - Video & Lesson Transcript

Ecological and socioeconomic factors associated with the human burden of environmentally mediated pathogens: a global analysis - The Lancet Planetary Health
PDF) Detection and characterization of zoonotic pathogens of free-ranging non-human primates from Zambia.
Recomendado para você
-
 Eduarda Silva Me beija renato Curtir Renato Ruiz Vem na minha casa WDOs: Curtir Eduarda Silva26 março 2025
Eduarda Silva Me beija renato Curtir Renato Ruiz Vem na minha casa WDOs: Curtir Eduarda Silva26 março 2025 -
 Renato Ruiz Há 7 horas Dormindo - iFunny Brazil26 março 2025
Renato Ruiz Há 7 horas Dormindo - iFunny Brazil26 março 2025 -
 Renato Ruiz26 março 2025
Renato Ruiz26 março 2025 -
renato ruiz meme|Pesquisa do TikTok26 março 2025
-
 Juruá Editora - Grito pela Democracia, O - Crimes Contra o Estado Democrático de Direito Brasileiro - Call for Democracy: Crimes Against the Brazilian Democratic Rule of Law, Coordenadora: Denise Hammerschmidt26 março 2025
Juruá Editora - Grito pela Democracia, O - Crimes Contra o Estado Democrático de Direito Brasileiro - Call for Democracy: Crimes Against the Brazilian Democratic Rule of Law, Coordenadora: Denise Hammerschmidt26 março 2025 -
 The Europeans (2020) - IMDb26 março 2025
The Europeans (2020) - IMDb26 março 2025 -
 Averno (wrestler) - Wikipedia26 março 2025
Averno (wrestler) - Wikipedia26 março 2025 -
 Sampaoli é um enganador caótico', detona Renato Mauricio Prado26 março 2025
Sampaoli é um enganador caótico', detona Renato Mauricio Prado26 março 2025 -
 Crime, Polícia e Justiça no Brasil26 março 2025
Crime, Polícia e Justiça no Brasil26 março 2025 -
 História Amor ou Amizade?? - Apresentação e Capítulo 1 - História escrita por New_moon2724 - Spirit Fanfics e Histórias26 março 2025
História Amor ou Amizade?? - Apresentação e Capítulo 1 - História escrita por New_moon2724 - Spirit Fanfics e Histórias26 março 2025
você pode gostar
-
 Manchester City vence o Estrela Vermelha de virada em estreia na Champions26 março 2025
Manchester City vence o Estrela Vermelha de virada em estreia na Champions26 março 2025 -
 Escola de samba paulista reproduz histórico Cavalo de Troia em26 março 2025
Escola de samba paulista reproduz histórico Cavalo de Troia em26 março 2025 -
 Uncharted: Drake's Fortune Full Gameplay Walkthrough [Longplay26 março 2025
Uncharted: Drake's Fortune Full Gameplay Walkthrough [Longplay26 março 2025 -
 Slavia Prague wallpaper. Football wallpaper, Wallpaper, ? logo26 março 2025
Slavia Prague wallpaper. Football wallpaper, Wallpaper, ? logo26 março 2025 -
 Shonen Jump News on X: ONE PIECE TV Anime has revealed a new Opening and Ending Themes for its upcoming Egghead Arc: · Opening: 'Aaah!' by Hiroshi Kitadani · Ending: 'Dear Sunrise26 março 2025
Shonen Jump News on X: ONE PIECE TV Anime has revealed a new Opening and Ending Themes for its upcoming Egghead Arc: · Opening: 'Aaah!' by Hiroshi Kitadani · Ending: 'Dear Sunrise26 março 2025 -
 Golden Time26 março 2025
Golden Time26 março 2025 -
![JAPANESE - English] Kyojin no Hoshi Chirashi : r/translator](https://i.redd.it/br6qa4dwiix61.jpg) JAPANESE - English] Kyojin no Hoshi Chirashi : r/translator26 março 2025
JAPANESE - English] Kyojin no Hoshi Chirashi : r/translator26 março 2025 -
 Goku de Dragon ball GT26 março 2025
Goku de Dragon ball GT26 março 2025 -
 Nightcall sheet music for voice, piano or guitar (PDF)26 março 2025
Nightcall sheet music for voice, piano or guitar (PDF)26 março 2025 -
 Serve o cartaz Segundo a nova regra ortografica plateia não tem mais acento WS AGORA TODOS FICAM EM26 março 2025
Serve o cartaz Segundo a nova regra ortografica plateia não tem mais acento WS AGORA TODOS FICAM EM26 março 2025
