Fiber deprivation and microbiome-borne curli shift gut bacterial populations and accelerate disease in a mouse model of Parkinson's disease - ScienceDirect
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 25 abril 2025

Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a neurological disorder characterized by motor dysfunction, dopaminergic neuron loss, and alpha-synuclein (αSyn) inclusion…

Fiber deprivation and microbiome-borne curli shift gut bacterial populations and accelerate disease in a mouse model of Parkinson's disease - ScienceDirect
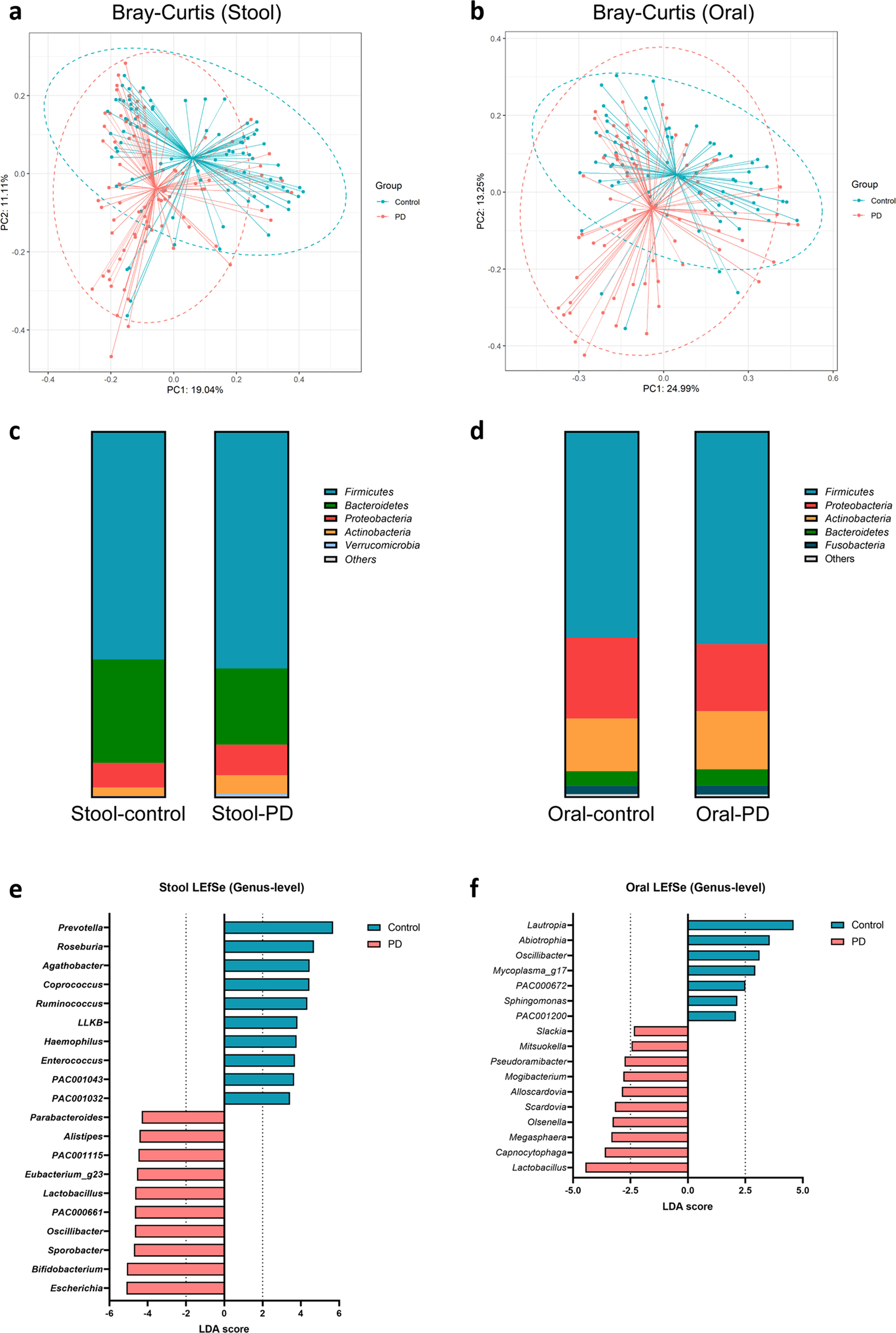
Oral and gut dysbiosis leads to functional alterations in Parkinson's disease
Frontiers Gut Microbiota Approach—A New Strategy to Treat Parkinson's Disease
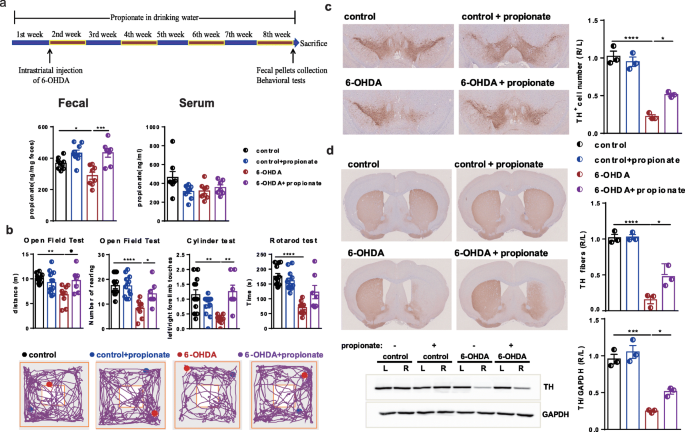
Gut microbiota-derived propionate mediates the neuroprotective effect of osteocalcin in a mouse model of Parkinson's disease, Microbiome
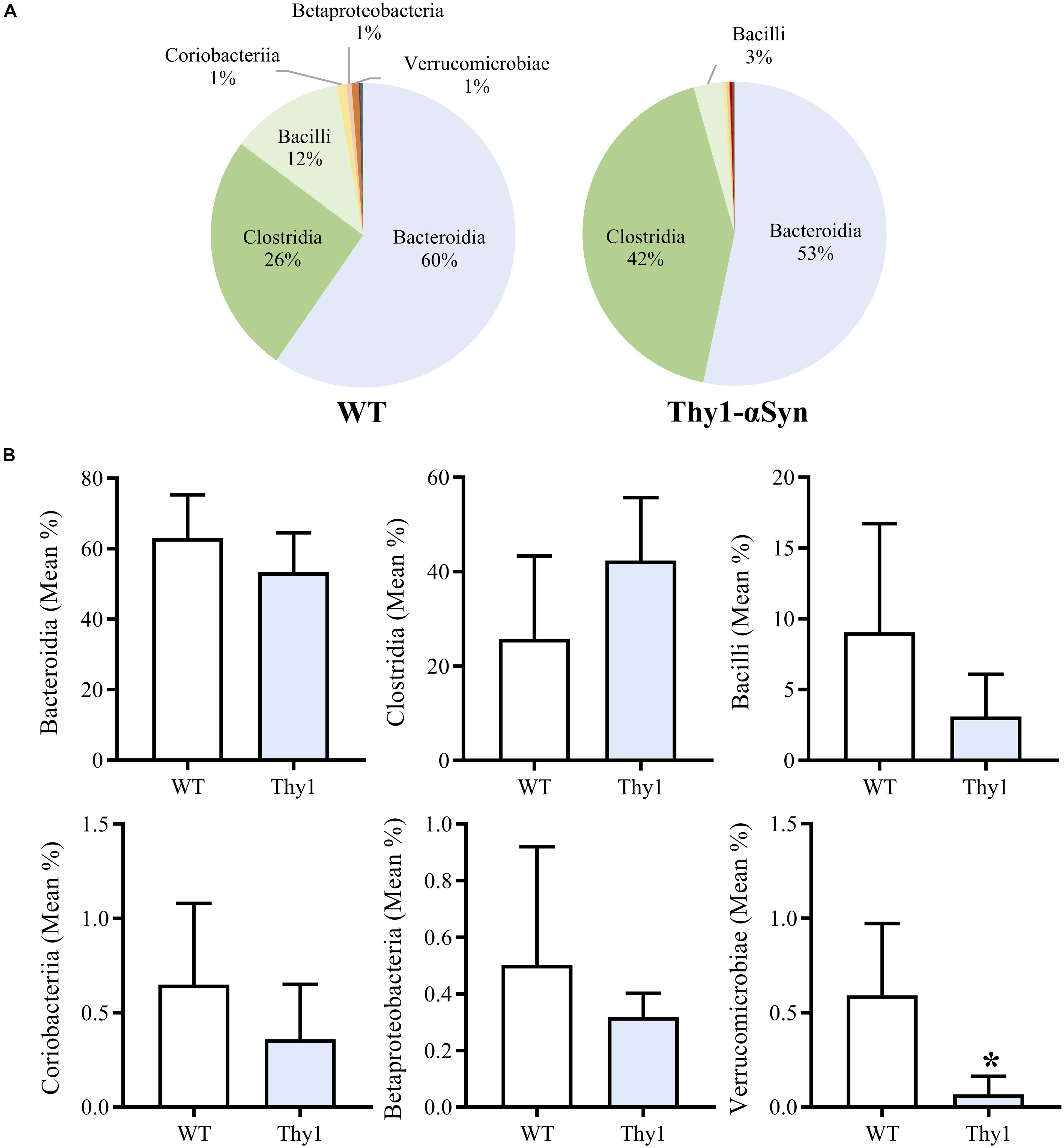
Frontiers Altered Gut Microbiome in Parkinson's Disease and the Influence of Lipopolysaccharide in a Human α-Synuclein Over-Expressing Mouse Model

Gut Microbiota Regulate Motor Deficits and Neuroinflammation in a Model of Parkinson's Disease - ScienceDirect

PDF) Dietary fibre deprivation and bacterial curli exposure shift gut microbiome and exacerbate Parkinson's disease-like pathologies in an alpha-synuclein-overexpressing mouse

Effect of Coffee against MPTP-Induced Motor Deficits and Neurodegeneration in Mice Via Regulating Gut Microbiota

Unravelling the role of gut microbiota in Parkinson's disease progression: Pathogenic and therapeutic implications - ScienceDirect
IJMS March-1 2021 - Browse Articles

Cell Reports, Vol 42, Issue 9, 26 September 2023

Gut Microbiota Regulate Motor Deficits and Neuroinflammation in a Model of Parkinson's Disease - ScienceDirect

Inflammation, stress, and gut-brain axis as therapeutic targets in bipolar disorder - ScienceDirect
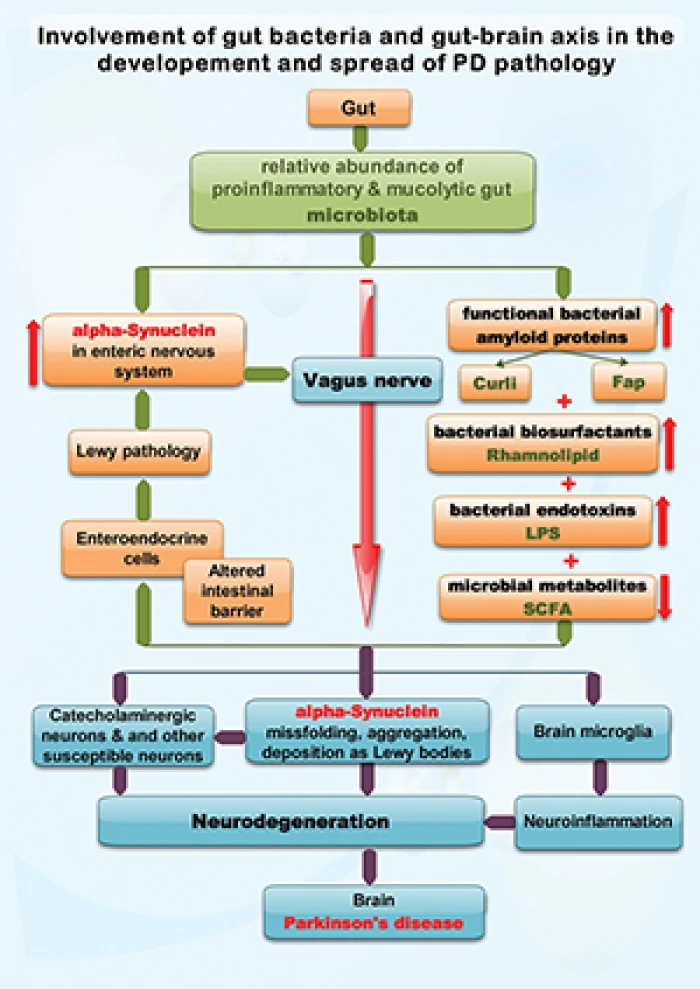
Potential roles of functional bacterial amyloid proteins, bacterial biosurfactants and other putative gut microbiota products in the etiopathogeny of Parkinson's Disease
Recomendado para você
-
Equipe Duda Games (@moderacaodg_) / X25 abril 2025
-
 DudaGames_ofc - Twitch25 abril 2025
DudaGames_ofc - Twitch25 abril 2025 -
Twitch25 abril 2025
-
SOLTEIRA E GADA. Iris gta rp!, gta rp!, By DUDÀ GAMES25 abril 2025
-
jujuba gta rp duda|Pesquisa do TikTok25 abril 2025
-
 Umbreon and Espeon Custom Nintendo Gameboy Advance Shell25 abril 2025
Umbreon and Espeon Custom Nintendo Gameboy Advance Shell25 abril 2025 -
 HP - Pavilion 15.6inch Gaming Laptop - AMD Ryzen 5 - 8GB Memory - NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1650 - 256GB SSD - Shadow Black, 15-ec1073d : Electronics25 abril 2025
HP - Pavilion 15.6inch Gaming Laptop - AMD Ryzen 5 - 8GB Memory - NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1650 - 256GB SSD - Shadow Black, 15-ec1073d : Electronics25 abril 2025 -
 Feminino Duda Machado - Calçados - Compre Já25 abril 2025
Feminino Duda Machado - Calçados - Compre Já25 abril 2025 -
 Desapego Games - Genshin Impact > CONTA AR57, COM 14 PERSONAGENS 5* (3 ARCONTES INCLUSOS) E 10 ARMAS 5* ESTRELAS25 abril 2025
Desapego Games - Genshin Impact > CONTA AR57, COM 14 PERSONAGENS 5* (3 ARCONTES INCLUSOS) E 10 ARMAS 5* ESTRELAS25 abril 2025 -
 Sandálias Feminino Multimarcas - Calçados - Compre Já25 abril 2025
Sandálias Feminino Multimarcas - Calçados - Compre Já25 abril 2025
você pode gostar
-
 Design De Logotipo De Comida De Pizza Logotipo De Serviço De Pizza25 abril 2025
Design De Logotipo De Comida De Pizza Logotipo De Serviço De Pizza25 abril 2025 -
 New Pokémon Snap - Lugia location, how to wake Lugia up and25 abril 2025
New Pokémon Snap - Lugia location, how to wake Lugia up and25 abril 2025 -
 A guide to Stremio, a middle ground between streaming and torrents : r/animepiracy25 abril 2025
A guide to Stremio, a middle ground between streaming and torrents : r/animepiracy25 abril 2025 -
:upscale()/2021/04/29/953/n/1922794/4e8bf3ca608b2a960da289.57932951_.jpg) Best Furniture With Storage From Wayfair 202125 abril 2025
Best Furniture With Storage From Wayfair 202125 abril 2025 -
 Molde de Silicone Xadrez25 abril 2025
Molde de Silicone Xadrez25 abril 2025 -
Meme Picrew25 abril 2025
-
 Detroit: Become Human PlayStation 4 Pro Review25 abril 2025
Detroit: Become Human PlayStation 4 Pro Review25 abril 2025 -
 Blox Fruits 2550 lvl Rabbit SuperHuman MAX Magma Spirit Fruit Control Fruit Pain Fruit Rumble Fruit Spider Fruit Ghost Fruit25 abril 2025
Blox Fruits 2550 lvl Rabbit SuperHuman MAX Magma Spirit Fruit Control Fruit Pain Fruit Rumble Fruit Spider Fruit Ghost Fruit25 abril 2025 -
 I FINALLY REACHED THE THIRD SEA! *Level 1500* Roblox Blox Fruits25 abril 2025
I FINALLY REACHED THE THIRD SEA! *Level 1500* Roblox Blox Fruits25 abril 2025 -
o que significa casal endgame|Pesquisa do TikTok25 abril 2025



